
Meet Our Grad Student Scholars is a series from Illinois-Indiana Sea Grant (IISG) celebrating the students and research funded by our scholars program. To learn more about our faculty and graduate student funding opportunities, visit Fellowships & Scholarships.
Xiaoli Xiong is a Ph.D. student in the School of Construction Management Technology at Purdue University and a recipient of the Ross Fellowship. He works under the guidance of Chengcheng Tao in the Sustainable Infrastructure and Manufacturing Lab. Xiong’s research focuses on the sustainable manufacturing of cement and concrete materials. Xiong’s IISG project investigates the feasibility of incorporating dredged sediments from Lake Michigan into cement mortar, aiming to use waste materials to develop more environmentally friendly cementitious products.
Concrete is the most extensively used material created by humans, with 14 billion cubic meters produced annually to satisfy a wide range of construction demands. However, its widespread use has considerable environmental consequences.
To address these challenges, many organizations have committed to achieving a net zero industry by 2050. In response to the escalating depletion of natural resources, the construction industry is actively seeking alternative materials to replace conventional cement and aggregate in 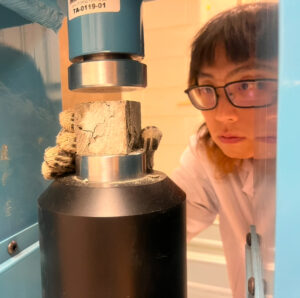 cementitious composites. Dredged sediments, consisting of inorganic and organic materials accumulating at the bottom of water bodies like the Great Lakes, offer a potential solution.
cementitious composites. Dredged sediments, consisting of inorganic and organic materials accumulating at the bottom of water bodies like the Great Lakes, offer a potential solution.
The rapid expansion of water transportation and port infrastructure in the Great Lakes region has led to the generation of substantial volumes of sediment. If left unaddressed, the accumulation of dredged sediments poses significant environmental risks, including water contamination, disruption of aquatic ecosystems, degradation of water quality, and adverse impacts on marine and human life.
Traditional methods of managing dredged sediments, such as dumping and landfilling, are inefficient and costly. As an alternative, researchers have proposed sediment solidification technology using cement and other binders. This method produces a solidified product with excellent mechanical properties that meet the standards for building materials.
Inspired by this approach, using dredged sediments in cementitious composites presents a promising opportunity. This not only mitigates the risk of secondary pollution from improper disposal but also reduces the construction industry’s reliance on natural resources, promoting a more sustainable future.
 In October 2024, Xiong and his colleagues collected samples from the shores of Lake Michigan. Currently, experiments are being meticulously conducted. The performance of dredged sediments in both cement paste and cement mortar is being evaluated through macro-mechanical testing methods, such as static compressive strength tests, and advanced micro-investigation techniques, including X-ray diffraction, X-ray fluorescence, and scanning electron microscopy.
In October 2024, Xiong and his colleagues collected samples from the shores of Lake Michigan. Currently, experiments are being meticulously conducted. The performance of dredged sediments in both cement paste and cement mortar is being evaluated through macro-mechanical testing methods, such as static compressive strength tests, and advanced micro-investigation techniques, including X-ray diffraction, X-ray fluorescence, and scanning electron microscopy.
“By recycling dredged sediments as aggregates or even as a potential cement replacement, we aim to create a new type of sustainable concrete product,” Xiong said. “We believe the results of this research could greatly benefit Lake Michigan’s ecosystem and its surrounding communities, which is why this study is both important and exciting for us.”
___________________________________________________________________________
Illinois-Indiana Sea Grant is one of 34 Sea Grant programs supported by the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration in coastal and Great Lakes states that encourage the wise stewardship of our marine resources through research, education, outreach and technology transfer. In partnership with the University of Illinois Extension, and Purdue University Forestry and Natural Resources, Illinois-Indiana Sea Grant brings science together with communities for solutions that work.

