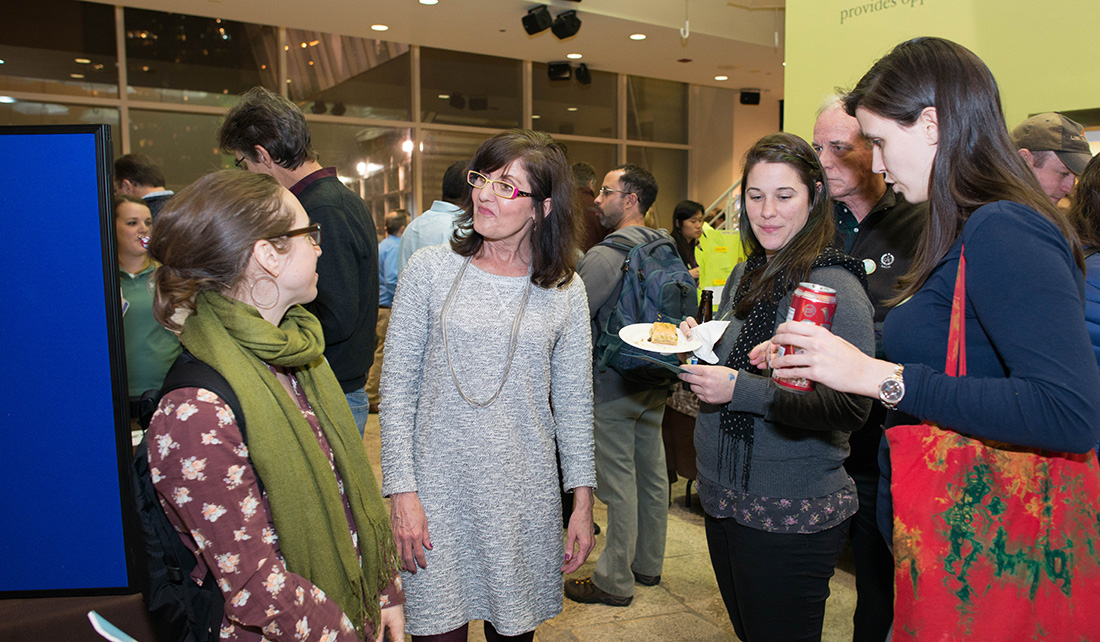The Center for Great Lakes Literacy (CGLL) teamed up with the Peggy Notebaert Nature Museum last month to host “Great Lakes Awareness Day: Lake Michigan’s Beauty & Fragility.” CGLL fosters a community of Great Lakes literate educators, students, scientists, environmental professionals, and citizen volunteers dedicated to improved Great Lakes stewardship.
The event featured Great Lakes education and outreach programs developed by Illinois-Indiana Sea Grant (IISG) specialists, as well as stewardship projects that CGLL-trained teachers have facilitated with their students.
Ayesha Qazi, a horticulture and biology student teacher at Robert Lindblom Math and Science Academy in Chicago, manned a table with her student to show off her “greenhouse” classroom. This new endeavor—that even she admits sounds a little “bizarre”—has proven to be extremely successful.
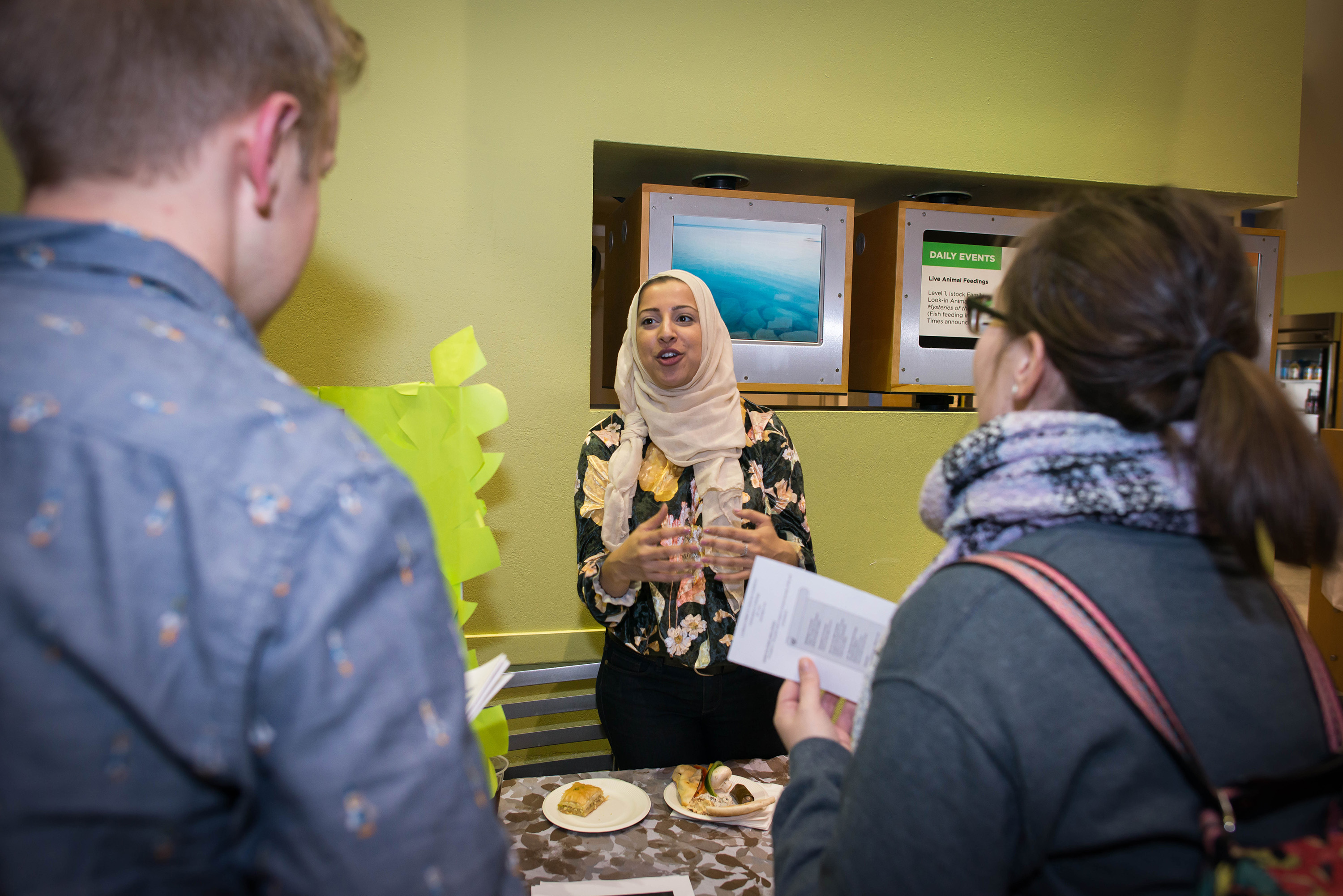

Ayesha Qazi, a horticulture and biology student teacher at Robert Lindblom Math and Science Academy in Chicago, talks about her greenhouse classroom.
Qazi took part in a CGLL workshop that fosters informed and responsible decisions to advance basin-wide stewardship by providing hands-on experiences, educational resources, and networking opportunities.
“I’m always in the greenhouse, so why don’t I have seating in the greenhouse,” Qazi asked herself.
Qazi said because many of her students don’t have easy access to green spaces, she created a classroom surrounded by lush plants, nice lighting, and fresh air.
And that became a complete game-changer.
“In class if the students get distracted, they’re in a greenhouse, they’re looking at plants. They say it’s so calm and peaceful.”
Christine Miller, a science teacher at Healy Elementary School in Chicago, brought three of her students to staff a table focusing on aquatic invasive species. Her students showcased what they learned about the invasive plant, purple loosestrife, that has crowded out native species in Illinois wetland and marsh areas.
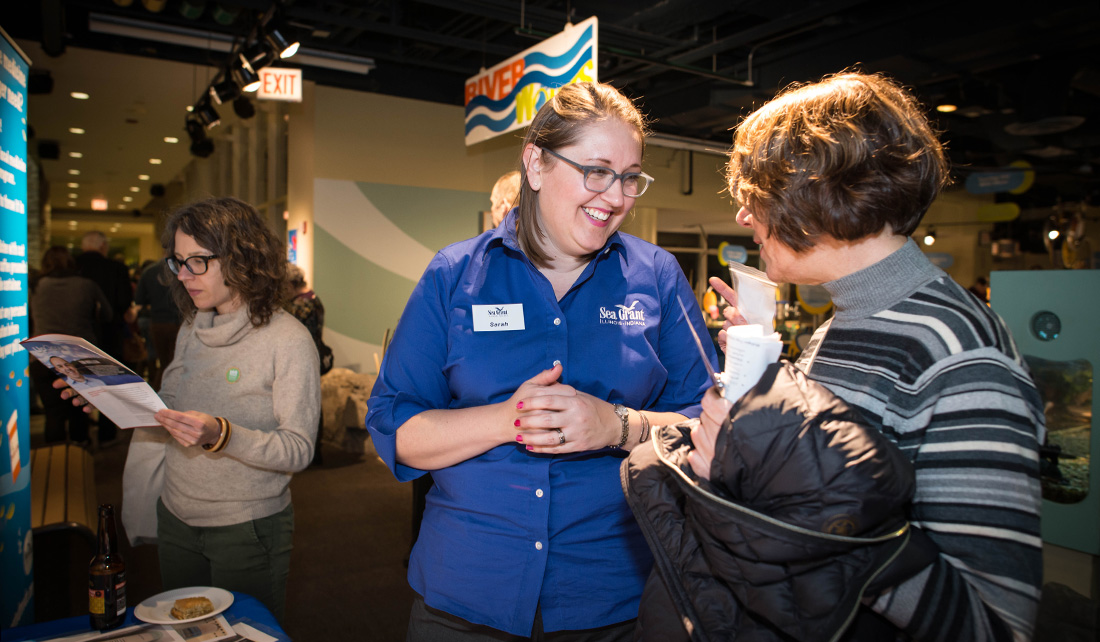

Sarah Zack, IISG pollution prevention outreach specialist, speaks to a woman at her table at the event.
“This event was a great reminder of how engaged people are in Great Lakes issues, and how important healthy water resources are to us all,” said Sarah Zack, IISG pollution prevention specialist who had a table at the event.
“Everyone I spoke to was interested in learning how they could do more to prevent pharmaceuticals and microplastics from entering our waters, which made for a really exciting event.”
IISG specialists Greg Hitzroth, Allison Neubauer, Kristin TePas, Molly Woloszyn, and Irene Miles also hosted tables at the event. Shipboard Science alumna Susie Hoffmann was there to share her photos from her U.S. EPA R/V Lake Guardian experience.
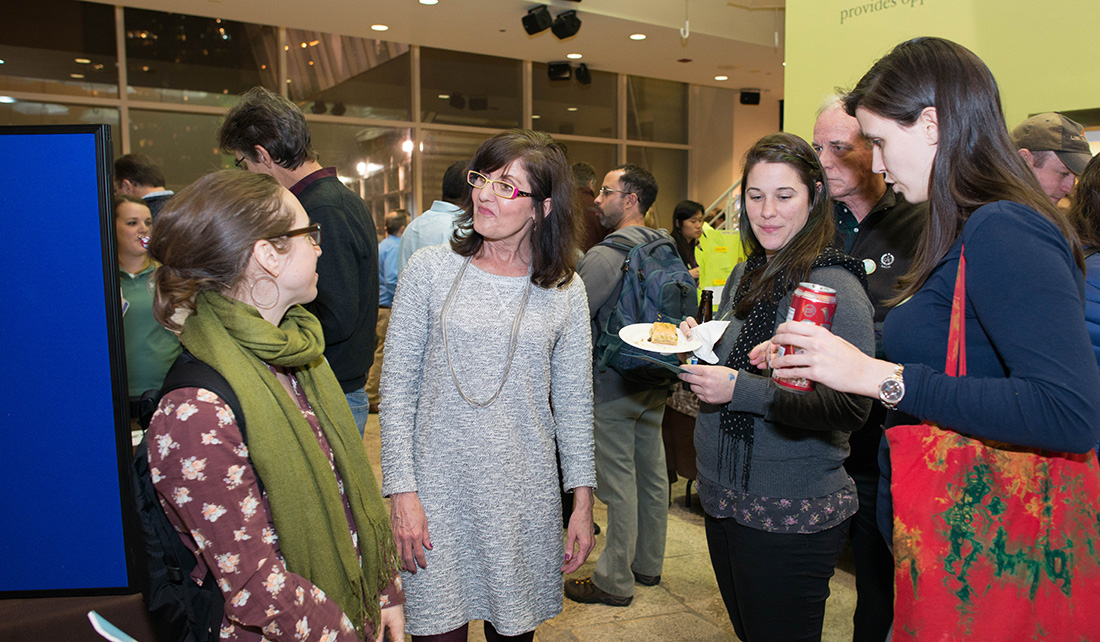
Terri Hallesy, IISG education coordinator, second from left, chats with women at the event.
“With increasing public concern about environmental issues, it is essential that we work together to build a scientifically literate citizenry,” said Terri Hallesy, IISG education coordinator. “Great Lakes Awareness Day events provide an opportunity to broaden understanding of Great Lakes issues to enable a greater number of citizens to become better stewards of the Great Lakes environment.”
“Our ultimate goal is to leave the Great Lakes better for the next generation.”
During the summer of 2014 sixteen science teachers from all around the Great Lakes region spent a week on board the U.S. E.P.A ship R/V Lake Guardian on Lake Erie as part of the Shipboard and Shoreline Science Workshop. Sponsored by the Center for Great Lakes Literacy, Ohio Sea Grant, Pennsylvania Sea Grant, and the U. S. Environmental Protection Agency, teachers were connected with scientists in first hand explorations of the ecology, geology, and bio-geochemical processes of Lake Erie.
Fifth grade middle school science teacher David Murduck was introduced to many ideas for his classroom and field activities from his experience on the research ship:

Although I knew the experience on the
R/V Guardian was going to be amazing, I never dreamed that the workshop would have such an impact on my students. Towards the beginning of the school year my class spends a lot of time learning about the importance of qualitative and quantitative observation. This year my students were able to apply their understanding of metric measurement while learning about the Great Lakes. Students were engaged in an activity where they had to use yarn to outline, label, and organize the shorelines of the Great Lakes to scale. After graphing the shoreline metric distances, students compared the total shoreline distances of the Great Lakes to the U.S. shoreline along the Atlantic Ocean, Pacific Ocean, and the Gulf of Mexico. Students then compared and contrasted the size of the Great Lakes to the total volume of water each lake holds, the metric mass of commercial fish caught, and the human population surrounding each Great Lake. This activity enabled me to reinforce the importance of metric measurement as we used metric rulers, triple-beam balances, and graduated cylinders in class. This also set the stage for in-depth discussion of the Great Lakes and the problems they face.
As the year progressed, students learned more about the Great Lakes, and specifically the Lake Erie watershed that they live in. Students learned about research that scientists aboard the R/V Guardian were completing. Research included a study of native and invasive species by Ruth Briland of The Ohio State University, a study of the presence of plastics by Sam Mason from State University of New York, and a study of chemicals and E. coli bacteria by Steve Mauro from Gannon University. This led to a better understanding of the importance of water quality. Macro-invertebrate studies and the use of water quality monitoring equipment lent for use by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency allowed real-world application as students studied water in local tributaries of the Lake Erie watershed.
Follow-up allowed students to complete individual in-depth research related to invasive species of the Great Lakes. This information was presented with the use of visual projects such as PowerPoint, dioramas, or posters in class.
Students then applied what they had learned throughout the year by participating in an important stewardship project. With a unique partnership between our school and the Cuyahoga Valley National Park, students planted native oak trees for the park. Park ranger John DeMuth came to each 5thgrade science class and discussed how the invasive Privot plant forces out native plants along the Cuyahoga River. He explained that native plants have deeper root systems that hold the soil more securely and slow erosion of the river banks. He also explained that unlike the past when pollution was the main
problem in the Cuyahoga River watershed, invasive species are now the real concern.
In culmination, with the help of high school horticulture students from the Trumbull County Technical and Career Center and park rangers from the Cuyahoga Valley National Park, my students learned teamwork as they used gloves, eye protection, and loppers supplied by the national park to cut and stack the invasive plants along the river bank. National park employees later use controlled use of herbicides on the stumps to kill the plants. What an amazing year!
A closer look at web tools and sites that boost research and empower Great Lakes communities to secure a healthy environment and economy.
For over two years, the Limno Loan program has been shaking up science class across the Great Lakes region. Coordinated by IISG and the U.S. EPA Great Lakes National Program Office, the program gives students an opportunity to collect water quality data from local waterways with the same kind of monitoring sensors used by scientist aboard the R/V Lake Guardian.

And now, teachers can take their Hydrolab projects one step further with help from IISG’s new Limno Loan site. In addition to information about the equipment and the parameters it measures, the site provides lessons and activities to help teachers K-12 better integrate the Hydrolab into their aquatic science sections.
The activities, most of which were created by educators who used the equipment in their own classrooms, focus on demonstrating the connections between water quality, aquatic food webs, and human activities. Sample water quality data sheets are also available. The website also provides a unique opportunity for classes to share their data and compare it to information collected by fellow students across the region.
New activities will be added as they are developed, so be sure to check back later. You can also read more about how the Limno Loan program has helped improve student understanding of Great Lakes sciences in our Winter 2012 Helm.
 Charleston, IL may be hundreds of miles from where the R/V Lake Guardian was collecting samples in Lake Erie earlier this week, but that didn’t stop a group of sixth graders from taking a tour of the U.S. EPA vessel. From the comfort of their classroom, more than 60 students and teachers watched as EPA researcher Beth Hinchey Malloy talked about living and working on a boat and showed them around.
Charleston, IL may be hundreds of miles from where the R/V Lake Guardian was collecting samples in Lake Erie earlier this week, but that didn’t stop a group of sixth graders from taking a tour of the U.S. EPA vessel. From the comfort of their classroom, more than 60 students and teachers watched as EPA researcher Beth Hinchey Malloy talked about living and working on a boat and showed them around.
 The tour started, of course, on the ship’s deck and quickly moved inside to the labs, where scientists took a break from processing samples to explain how studying bug populations helps researchers judge the health of aquatic ecosystems. From there it was on to the galley to see what’s for lunch and up to the bridge to chat with the captain.
The tour started, of course, on the ship’s deck and quickly moved inside to the labs, where scientists took a break from processing samples to explain how studying bug populations helps researchers judge the health of aquatic ecosystems. From there it was on to the galley to see what’s for lunch and up to the bridge to chat with the captain.

And the students had more than a few questions, particularly for the captain—Is it easy to drive the boat? How can you tell how deep the water is? Where does the Lake Guardian go?
Students also got a sneak peak at the type of equipment they will use later this year to collect data on water characteristics like dissolved oxygen, conductivity, and pH. Their teacher, Pamela Evans, is one of several scheduled to use the Hydrolab to make science class more hands-on this year.
The event ended after a jam-packed 30 minutes because another class was waiting on deck to take the tour. In fact, eight classes across the Great Lakes region got a first-hand look at the Lake Guardian this week. And this is just the beginning. The research vessel will soon dock for the winter, but video chats with EPA scientists will continue throughout the school year.
The video chats and equipment loan program are all part of efforts by IISG and the EPA Great Lakes National Program Office to boost Great Lakes education. Teachers were introduced to the programs, along with other classroom resources, during the annual Shipboard Science workshop.