May 2nd, 2017 by IISG
St. Elmo Brady STEM Academy welcomed two IISG specialists to their roster of teachers recently.
Climate Specialist Molly Woloszyn and Education Coordinator Terri Hallesy carried on in the spirit of the academy by sharing their expertise with underrepresented fourth- and fifth-grade students in the Champaign, Illinois area.
The program was developed in 2013 by Ricky Greer, a K-12 education specialist, and Dr. Jerrod A. Henderson, a University of Illinois lecturer in Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering (CHBE). Its name, St. Elmo Brady, honors the first African-American student to earn a PhD in chemistry in the United States in 1916. Although the program is housed in CHBE, it’s meant to introduce students to a range of STEM disciplines.
Woloszyn and the students toured the weather station with Jim Angel, the Illinois state climatologist. She also did an activity that demonstrated air pressure – the collapsing can. She then taught them how to make a rain gauge from a 2-liter bottle that they could take home.
“I had a really great time doing this event,” Woloszyn said. “It was really fun to interact with the students and see them be so interested in making the rain gauge.”
Hallesy spent her time with the students talking about the role aquatic invasive species play in altering the Great Lakes basin ecosystem. She used fun games like “Stop Asian Carp in their Tracks” and “Nab the Aquatic Invader,” to explain how students by making simple changes, like properly disposing of a pet fish, can do their part in helping to prevent the spread of AIS.
“I see them as agents for change in their community. The kids were so interested in learning about what they could do to help,” Hallesy said. “They loved it!”
Program director Joe Gamez has seen the positive impact the program has had on the students.
“Without this exposure, minorities and girls think, ‘Oh, this this is not for me. This is for other people. Other people do that kind of stuff,’” Gamez said.
“But when they get exposure to it, it changes the way they look at things. The exposure the children get to these STEM topics from people who are so knowledgeable and passionate has really made a difference.”
May 2nd, 2016 by IISG
Every spring, The Sun Foundation invites students, teachers, community leaders, and the general public to attend the Clean Water Celebration at the Peoria Civic Center. Through engaging hands-on activities and exhibits, this gathering encourages students and the public to learn how to improve water quality, to think critically and creatively about water conservation issues, and to protect and sustain our natural resources.
IISG educators, Terri Hallesy and Kirsten Walker, challenged students to tackle the issue of Asian carp invading new areas through IISG’s “Stop Asian Carp in Their Tracks” activity, a video about Asian carp in Illinois, and the website Nab the Aquatic Invader!
Presenters shared information about how this troublesome invader competes with native fish by eating lots of phytoplankton and zooplankton, the base of the food chain. Students learned how carp – which can weigh up to 60 pounds – become startled by boat motors and jump out of the water, smacking nearby boaters and anglers.
In small groups, students also discussed the location of Asian carp’s native habitat, how they arrived in the Midwest, and strategies to help reduce their populations. Students gained an understanding about the ways in which invasive species are introduced, the competitive advantages they have in their new ecosystems, and their huge impact on an area’s natural biodiversity.
As a result of these activities, students were equipped as agents for change to engage family and community members in understanding how they, too, can play an important role in stopping the spread of aquatic invaders.
May 11th, 2015 by iisg_superadmin
Steve Park was one of 15 Great Lakes educators to set sail on Lake Erie last year for the annual Shipboard Science Workshop. Today, we hear a little of what he and his 7th grade students have been up to since.
 As a veteran teacher of enthusiastic middle school students, I adhere to Albert Einstein’s quote, “I never teach my pupils. I only attempt to provide the conditions in which they can learn.”
As a veteran teacher of enthusiastic middle school students, I adhere to Albert Einstein’s quote, “I never teach my pupils. I only attempt to provide the conditions in which they can learn.”
This school year started just like the first 20 years of my teaching career, with our study of environment science. However, it didn’t take long for my students to realize that the learning experiences this year were going to be extra special. Armed with a weeks worth of intense professional development while living on the R/V Lake Guardian motoring around Lake Erie, I had the resources, experiences, knowledge, and support to provide my students with the incredible conditions necessary for them to learn.
When teaching about the environment and stewardship, I have two goals. First, I want students to know specifically how they impact their local and global environments. Second, I want students to know how they can have a positive influence on their local and global environments. With that in mind, my students began their study on water ecology by conducting a video conference with individuals aboard the Lake Guardian collecting water samples in Lake St. Clair. Students learned about life on the Lake Guardian, research that is being done on the lake, and the responsibilities of the scientists.
Our focus then turned to our own outdoor classroom, where we have 36 acres of land, a large river, and a couple of smaller creeks. I intentionally set up conditions where my students had numerous opportunities to learn about the physical, chemical, and biological characteristics of the environment. In addition to traditional sampling techniques, my students conducted independent research projects. For instance, one group wanted to know if the diversity of macro invertebrates changed the farther you got from shore. To test their hypothesis, they created Hester-Dendy samplers and deployed them at various locations and distances from shore. Another group wanted to see if they could use all-natural materials to create a filter capable of reducing the turbidity of our river water to the World Health Organization standard of 5 ppm.

Currently, because of my interactions with Dr. Sam Mason on board the Lake Guardian last summer, my students have received a grant to study the plastic microbeads in our river water. Students will design, construct, and deploy collection seines to help determine the prevalence of these plastics in our water ecosystem.
As a society, we have a long, uphill climb when it comes to improving the quality of our wonderful Great Lakes. However, I am confident that the experiences I had during the Lake Erie Shipboard Science Workshop, the connections I made with incredibly supportive people, and the high quality curricular materials and equipment I received will provide my students with the conditions in which they can learn. This, in turn, will make that climb a little bit easier.
***Photo A: Students hear from a fishery biologist about the importance of fish stocking and how the technique is being used to study invasive species like Asian carp.
***Photo B: Students get their hands dirty learning about macro invertebrates.
March 11th, 2015 by iisg_superadmin
Earlier this year, AP science students at Chicago’s Lane Tech College Prep traded in their textbooks for field equipment to study water quality in the North Branch of the Chicago River. The Hydrolab allows students to monitor water characteristics like dissolved oxygen, pH, and conductivity with sensors similar to those used by scientists at the EPA Great Lakes National Program Office. The teacher, Dianne Lebryk, borrowed the equipment through the Limno Loan program to help students better understand the connection between water quality and man-made landscapes.
Several students wrote in to share their experiences working with the Hydrolab. We wrap things up today with Gayin Au.
Under the circumstances of an extremely frosty cold weather, our environmental classmates were still very eager to head out and experience the Hydrolab. As soon as we reached the river by our school, we saw a lot of trash in the river. The water looked very dense and had a very dark green color.
Two people were responsible for holding the Hydrolab since it was quite heavy. The others stood back to watch. I was surprised that we were able to get results really quick; at first I thought it would take a lot of time to process the information.
Goose poop, which is high in nitrate, dissolves and mixes into the water and plants use this nitrogen to keep them nice and fertilized. However, the river is also greatly harming the living things in it. The water lacked oxygen, meaning it will be more difficult for living things in there to survive. It also might mean there aren’t enough plants underwater to keep the normal level of oxygen up. It was greatly contaminated, and fish and other organisms will be affected, making them act unusually.
The lab was really quick and useful. It showed us the oxygen level, how much algae is in there, how polluted the river is in general, and more. The river goes by so many things that can affect it. Human trash, fertilizer, and goose poop (common near our school thanks to large fields of grass) all affect the quality of water.
January 14th, 2015 by iisg_superadmin
A closer look at web tools and sites that boost research and empower Great Lakes communities to secure a healthy environment and economy.
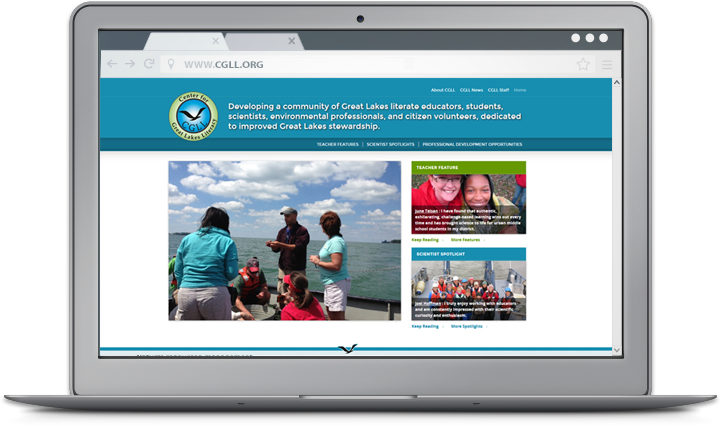.png) Educators interested in strengthening aquatic science programs and encouraging Great Lakes stewardship—look no further than the new Center for Great Lakes Literacy (CGLL) website.
Educators interested in strengthening aquatic science programs and encouraging Great Lakes stewardship—look no further than the new Center for Great Lakes Literacy (CGLL) website.
Created by Sea Grant educators throughout the region, the site is a one-stop-shop for classroom activities designed to boost Great Lakes literacy. Educators will find information on and links to teacher-tested curriculum like Fresh and Salt and Estuaries 101. And the Teacher Feature allows visitors to hear about education success stories directly from colleagues across the region.
Visitors to the site can also learn about the latest professional development opportunities available throughout the region. For example, teachers interested in the annual Shipboard Science Workshop, held this year on Lake Michigan, can find workshop information and application deadlines. Featured blogs also make it possible to read about teacher experiences at past CGLL workshops and follow along with the latest projects.
For more information on upcoming educator workshops and available curriculum, contact Terri Hallesy.
December 10th, 2014 by iisg_superadmin
A closer look at web tools and sites that boost research and empower Great Lakes communities to secure a healthy environment and economy.
It’s getting a little chilly for a stroll in the Windy City, but don’t let that stop you from enjoying it’s beautiful downtown lakefront. With Chicago Water Walk, you can explore some of the city’s most celebrated sites—Navy Pier, the Chicago River, downtown marinas, Buckingham Fountain, and Museum Campus—from anywhere.
The mobile-friendly website takes viewers on a journey through time to discover how Lake Michigan and the Chicago River transformed a small trading post into one of the economic and cultural hubs of the world—and the vital role these natural resources play in the city’s present and future.
Each stop in the virtual tour combines history, current events, and water sciences with fun facts to show the importance of aquatic ecosystems in the city’s past, present, and future. Stunning photos, historical images, and links to videos and other resources bring these issues to life and reveal a lakefront that will surprise even lifelong Chicagoans.
Visit the website and you’ll learn why the decision to reverse the Chicago River is still making waves more than a century later, how a city that sits along Lake Michigan can be concerned about having enough water in the future, and how native trees and plants are helping the city prepare for changing weather patterns. You’ll also hear about efforts to restore much-needed habitats for millions of birds, fish, and other wildlife.
And for those willing to brave the cold, a mobile tour app is available for free on Apple devices. You can follow the suggested routes or visit the sites that most appeal to you using the app’s interactive map.
The Chicago Water Walk website and app were developed by Illinois-Indiana Sea Grant with funding from the Illinois Department of Natural Resources Coastal Management Program and technical support from the University of Illinois Administrative Information Technology Services.
September 29th, 2014 by iisg_superadmin
Caitie McCoy, our environmental social scientist, writes in today to tell us about a unique education experience:
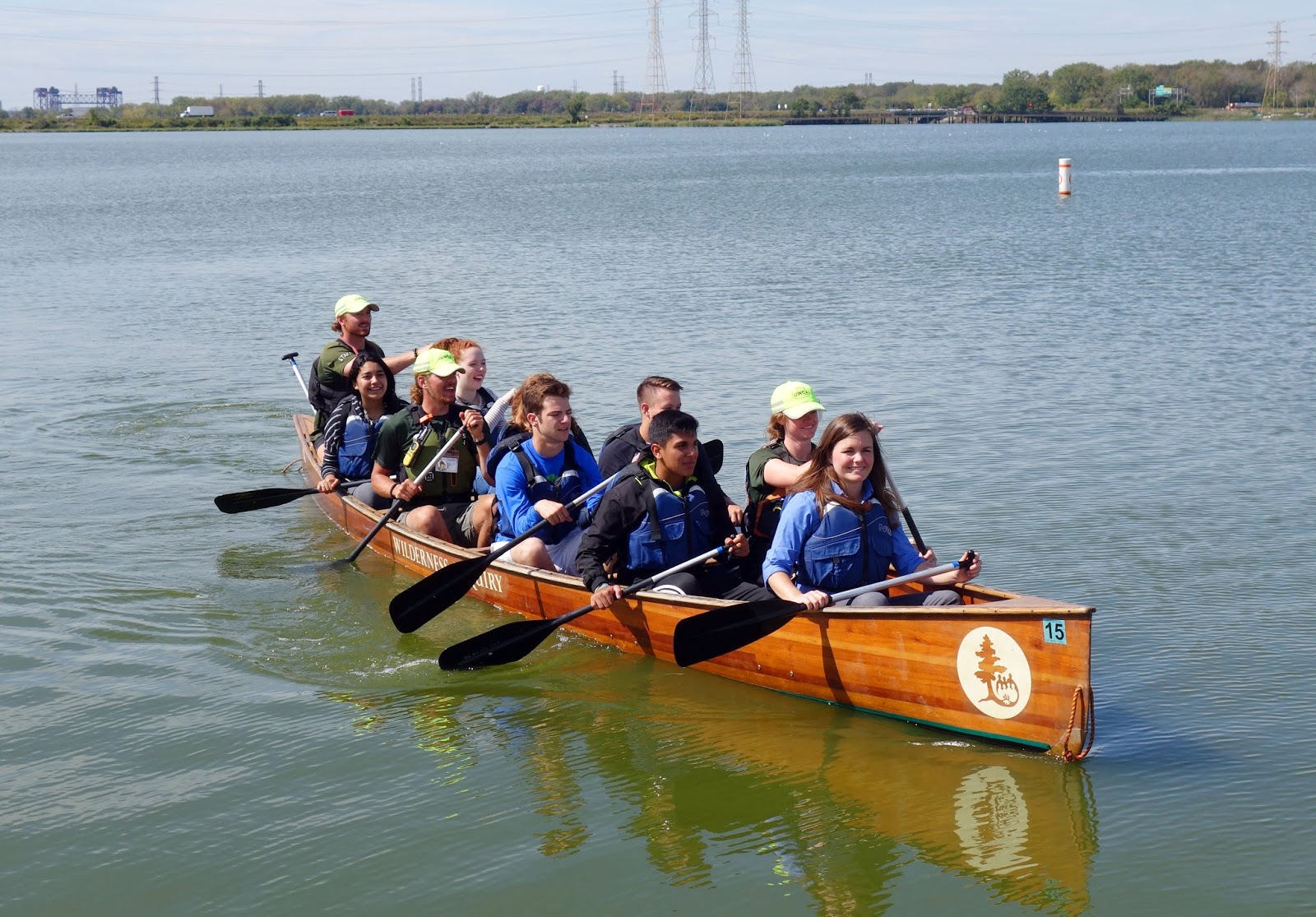
Last week, I ventured out of the office and into the field to hit the waters of the recently restored Wolf Lake with about 200 students from Hammond, IN. The weather was perfect for two days of canoeing and environmental education. Compassion for nature starts in childhood, so when asked by some partners at U.S. EPA, I jumped at the chance to help provide youth with such a meaningful outdoor experience.
We began our first day with an energetic greeting from Wilderness Inquiry, a national non-profit that aims to get as many city kids on the water as possible. The majority of the students had never been on any kind of boat before, but a friendly sun and slight breeze helped to calm a lot of nerves.
Students went out on the canoes in waves throughout the day, learning how to paddle and touring many restoration features. There were a lot of beautiful sites to see, including an egret that sat as still as a statue for hours on an island full of colorful native plants. Goldenrod, blue asters, and red maples dotted the landscape. With all the natural beauty surrounding us, we almost forgot that we were located in the middle of one of the country’s top industrial powerhouses .
The EPA team and I stayed busy providing the students with learning experiences as they waited for their turn on the canoes. We brought the Enviroscape, and it was a hit. Students loved the interactive nature of the game and learned a lot about their local watershed and what they can do to protect it from different pollution sources. We also took them on hikes by the lake, picking up litter and identifying different plant species.
 We had a lot of fun teaching, but I must admit, the highlight of my two days at Wolf Lake was jumping into a canoe and paddling around on the calm water with the students. It was rewarding to see high school students drop their guard and excitedly point out different shorebirds or hear them discuss the need to clean up the pollution in northwest Indiana, completely unprompted by an adult.
We had a lot of fun teaching, but I must admit, the highlight of my two days at Wolf Lake was jumping into a canoe and paddling around on the calm water with the students. It was rewarding to see high school students drop their guard and excitedly point out different shorebirds or hear them discuss the need to clean up the pollution in northwest Indiana, completely unprompted by an adult.
I’m grateful for our partnership with Wilderness Inquiry, and I hope to join them again next year. The opportunity is just too meaningful to miss!
September 25th, 2014 by iisg_superadmin
 Charleston, IL may be hundreds of miles from where the R/V Lake Guardian was collecting samples in Lake Erie earlier this week, but that didn’t stop a group of sixth graders from taking a tour of the U.S. EPA vessel. From the comfort of their classroom, more than 60 students and teachers watched as EPA researcher Beth Hinchey Malloy talked about living and working on a boat and showed them around.
Charleston, IL may be hundreds of miles from where the R/V Lake Guardian was collecting samples in Lake Erie earlier this week, but that didn’t stop a group of sixth graders from taking a tour of the U.S. EPA vessel. From the comfort of their classroom, more than 60 students and teachers watched as EPA researcher Beth Hinchey Malloy talked about living and working on a boat and showed them around.
 The tour started, of course, on the ship’s deck and quickly moved inside to the labs, where scientists took a break from processing samples to explain how studying bug populations helps researchers judge the health of aquatic ecosystems. From there it was on to the galley to see what’s for lunch and up to the bridge to chat with the captain.
The tour started, of course, on the ship’s deck and quickly moved inside to the labs, where scientists took a break from processing samples to explain how studying bug populations helps researchers judge the health of aquatic ecosystems. From there it was on to the galley to see what’s for lunch and up to the bridge to chat with the captain.

And the students had more than a few questions, particularly for the captain—Is it easy to drive the boat? How can you tell how deep the water is? Where does the Lake Guardian go?
Students also got a sneak peak at the type of equipment they will use later this year to collect data on water characteristics like dissolved oxygen, conductivity, and pH. Their teacher, Pamela Evans, is one of several scheduled to use the Hydrolab to make science class more hands-on this year.
The event ended after a jam-packed 30 minutes because another class was waiting on deck to take the tour. In fact, eight classes across the Great Lakes region got a first-hand look at the Lake Guardian this week. And this is just the beginning. The research vessel will soon dock for the winter, but video chats with EPA scientists will continue throughout the school year.
The video chats and equipment loan program are all part of efforts by IISG and the EPA Great Lakes National Program Office to boost Great Lakes education. Teachers were introduced to the programs, along with other classroom resources, during the annual Shipboard Science workshop.
September 16th, 2014 by iisg_superadmin
Our education team is at it again! Allison Neubauer wrote in with this exciting announcement:
 Teachers across the Great Lakes region—have we got a treat for you! You can now explore creative projects from all-star educators to spark new ideas and read important tips for getting your students involved in the effort to “nab” local aquatic invaders.
Teachers across the Great Lakes region—have we got a treat for you! You can now explore creative projects from all-star educators to spark new ideas and read important tips for getting your students involved in the effort to “nab” local aquatic invaders.
The IISG education team has been working hard to compile model projects that successfully tie together AIS education and community stewardship. Our revamped Nab the Aquatic Invader! website will help you up your game—and the new-and-improved Top Desk Administrator is your one-stop-shop for project ideas.
Community stewardship projects like the ones highlighted here are an exceptional tool for pushing students beyond rote memorization and providing them with an opportunity to apply their knowledge in ways that have positive impacts on their communities.
Preview outstanding examples of student work, ranging from fun informational activity books to catchy musical compilations. When you’re done perusing, read the summary reports written by the teachers responsible for these successful activities for information on how to plan and implement similar projects in your own classroom.
The Nab the Aquatic Invader! website is the place for the latest and greatest invasive species project models, information, and activities.



.png)










