December 19th, 2019 by Irene Miles
As 2019 draws to a close, I’m pleased to report that here at Illinois-Indiana Sea Grant, we’ve had a very good year, and that remained the case through the latter months.
In October, IISG underwent its program site review, which takes place every four years. Through this process, we presented our work from our last omnibus as well as our current activities to the external site review team. The review provides a great opportunity to reflect on our accomplishments and to look forward to new efforts.
The review team was very positive in its response, which, in large part, is due to not only the hard work of the IISG team, but also the great amount of support from our diverse partners, many of whom directly participated in the review.
This fall, we expanded our communication tools and products to share information about the Great Lakes with wider audiences. Inspired by a rich collection of photographs taken by Peter Essick, who works with National Geographic, IISG led the development of a photo essay called Great Lakes Resurgence about Areas of Concern in the region. The Great Lakes Sea Grant Network collaborated to tell the stories of these degraded waterways, to describe the progress of cleanup efforts and report local impacts of coastal restoration.
IISG now has a monthly podcast series, Teach Me about the Great Lakes, which debuted in December. Hosted by Stuart Carlton, the program’s assistant director, the podcast helps Stuart—and listeners—learn about the biology, ecology and natural history of the Great Lakes. Stuart is a social scientist who grew up in the south, so he is fairly new to Great Lakes issues. The first installment dove into concerns about microplastics, which have been found in the Great Lakes and many waterways all over the world. The next episode, available in early January, will focus on the geological history of the Great Lakes.
Autumn also brought awards season for the Sea Grant program, both regionally and nationally. We are proud of Pollution Prevention Specialist Sarah Zack, who was honored with the Great Lakes Sea Grant Network Early Career Award at the regional meeting in Sault St. Marie, Michigan. Irene Miles, strategic communication coordinator, won the Communications Service Award at the Sea Grant Extension Assembly, Communicator and Research Coordinator Conference in Savannah, Georgia. Also at the Savannah meeting, Brian Miller, IISG’s former director, was selected for the William Q. Wick Visionary Career Leadership Award, one of Sea Grant’s most prestigious honors.
As we all look forward to 2020, we wish you the best in the new year. For IISG, 2020 will bring an even greater focus to Lake Michigan. Scientists from around the Great Lakes basin will converge on the lake to conduct intensive research through the Cooperative Science and Monitoring Initiative (CSMI). IISG has just released an ESRI story map, Lake Michigan Health: A Deeper Dive, to share the results from the 2015 CSMI field year on Lake Michigan.
The Shipboard Science Workshop will also take place on Lake Michigan in the coming year. During this week-long workshop on the EPA research vessel the Lake Guardian, organized through the Center for Great Lakes Literacy, teachers from the region work side by side with scientists to study one of the Great Lakes. This coming year they set sail on Lake Michigan. We look forward to new science and stories that will emerge from both of these exciting initiatives.
Tomas Höök
Director, Illinois-Indiana Sea Grant
Illinois-Indiana Sea Grant is a part of University of Illinois Extension and Purdue Extension.
January 24th, 2017 by IISG
“It was an early morning start with sampling near Stony Point along the northern shores of Minnesota,” Ann Quinn, of Pennsylvania and Krysta Maas, of Minnesota, wrote in a blog post in July of 2016.
“As we approached Duluth, we stopped three times to sample near the shore and within the harbor. As we passed under the lift bridge, we could ‘clearly see’ the sediment plume from Monday night’s tremendous storm.”
Quinn and Maas were two of the 15 educators chosen last year to participate in the annual Shipboard Science Workshop aboard the U.S. EPA’s largest research and monitoring vessel on the Great Lakes, R/V Lake Guardian. Sea Grant’s Center for Great Lakes Literacy (CGLL) with U.S. EPA Great Lakes National Program Office (GLNPO) host the annual program. CGLL, formerly known of Centers for Ocean Science and Educational Exploration, is a collaborative effort led by Sea Grant educators throughout the Great Lakes watershed. This cruise is an important cornerstone of CGLL’s programming.
Every summer since 2006, CGLL joins forces with GLNPO to facilitate this weeklong workshop on one of the Great Lakes. Educators from not only traditional classrooms but also from places like museums, zoos and nature centers are welcome. The experience provides educators in the Great Lakes basin the opportunity to actually “do” science alongside aquatic researchers and learn strategies to integrate Great Lakes science into their curriculum.
IISG community outreach specialist Kristin TePas, who as the Sea Grant liaison with GLNPO accompanies every cruise, never tires of seeing teachers learning and researching in the field.
“I always look forward to watching how the educators take to the whole experience,” TePas said. “They come on rather green and leave at the end of the week looking like they have always lived on the ship, working like a well-oiled machine, taking part in field sampling and then analyzing in the lab.”
The hands-on, immersive nature of the experience fosters a broader and deeper understanding of science by integrating knowledge and research to enhance the teachers’ scientific investigation skills. Educators also expand their “treasure box” of lessons, teaching strategies, and network of like-minded colleagues.
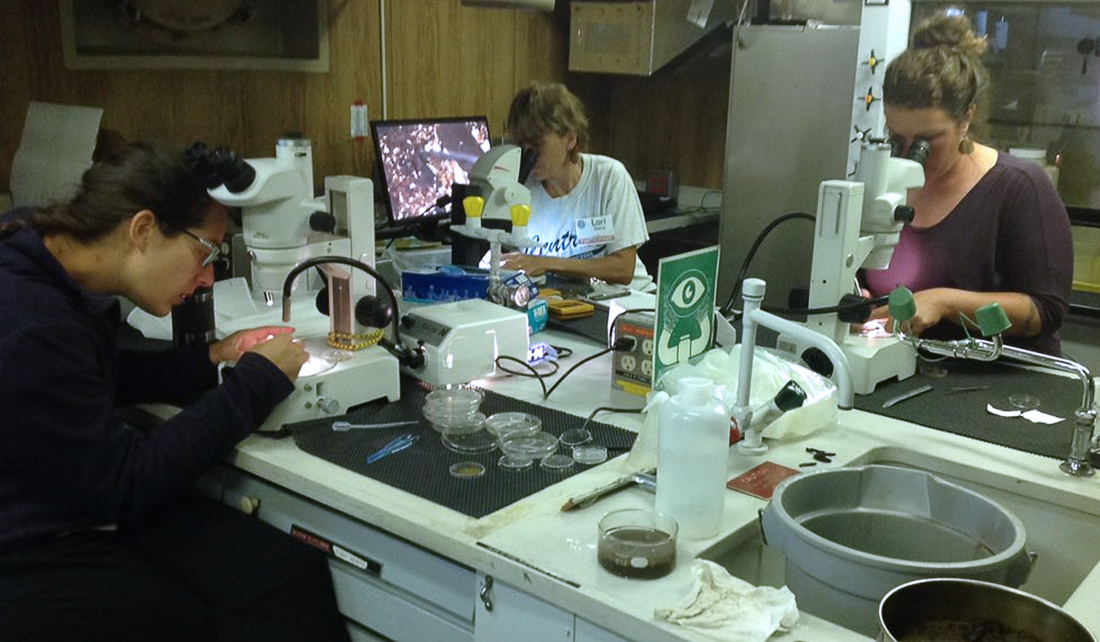

Following their time aboard the R/V Lake Guardian, the teachers return to their classroom with newfound knowledge that they then implement into school initiatives, like organizing cleanups of nearby natural areas, starting real-world data collection and analysis for class projects, bringing scientists into the classroom to talk and work with students, and inspiring school science and environmental clubs.
Alex Valencic, an alumnus of the 2013 Lake Ontario cruise, incorporated his experience into his fourth-grade class in Illinois.
Each student spent six weeks studying a freshwater fish found in the Great Lakes and learned about its appearance, habitat, life cycle, and where it falls in the food web.
“My primary goal is for my students to understand the rich diversity of life that lives within the Great Lakes-St. Lawrence River Seaway,” he said. “Even though we don’t live right on a lake, Illinois is hugely impacted by Lake Michigan.”
Educators and scientists on recent cruises have taken advantage of a new way to communicate their experiences to those back on land. In addition to filing blog posts on the CGLL website, folks on the cruise have started using Twitter to document their journey while traversing the lake. Illinois-Indiana Sea Grant Educator Allison Neubauer has compiled the tweets into a narrative of the cruise.
“Showing off the collaboration as it’s happening, making it accessible and informative,” Neubauer said, “is a great way to tell the important story of the work being done by the teachers and researchers in only seven days.”
The scientists onboard were equally impressed with the experience.
“A strong scientist-educator connection can bring the research alive as scientists share stories from the field or lab,” wrote Wisconsin researcher Emily Tyner in “Scientist Spotlights,” an ongoing series on the CGLL website.
“But the sharing process isn’t one-way,” Tyner pointed out. “Educators can offer a new and helpful way of looking at problems that stump scientists. Thinking back on my Lake Guardian cruise, the educators helped us gain helpful perspective when we faced hours trying to determine the problems with our experimental setup.”
The educators no doubt would agree. They get the chance—as many have put it—to take part in an adventurous, educational, inspiring, fun, and once-in-a-lifetime adventure!
Illinois-Indiana Sea Grant is a part of University of Illinois Extension and Purdue Extension.
October 4th, 2016 by IISG
Every month, the Center for Great Lakes Literacy (CGLL), a close partner with IISG, selects an outstanding scientist who embodies the CGLL mission and inspires people to take action to improve the health of the Great Lakes watershed.
This post originally appeared on the CGLL website.
Tim Hoellein
Associate Professor
Research Institution: Loyola University Chicago
Home state: Illinois
What got you interested in science and how did you end up as a Great Lakes scientist?
My interest in ecology is firmly rooted in where I’m from. I grew up in Edinboro, Pennsylvania, near Erie, and later lived in Pittsburgh and went to college in Buckhannon, West Virginia. My experiences in natural areas were places like Presque Isle, Point State Park, and Seneca Rocks. These are some of the most beautiful places in the world. The lakes, hills, rivers, and four seasons speak directly towards a sense of identity for those of us from the area. It is a landscape of extremes, because this region also has a heritage of heavy industry. Manufacturing and mining are important components of our cultural identity and provide the basis for commerce and quality of life. However, the history of mineral extraction, manufacturing, and contaminant storage left a legacy of insidious pollution throughout the region. My motivation for research in water pollution is rooted in that view so common in the Great Lakes and western Pennsylvania: the green and blue of Presque Isle in one direction and the smoke and metal of Erie’s industrial waterfront in the other. My overarching career goal is to work towards a restoration of ecological integrity within the urban and industrial areas where we work and live.
Describe your research related to the Great Lakes.
I study the interaction between common pollutants and the organisms living in streams and rivers of the Great Lakes region. Water quality in the lakes strongly depends on what we put into the tributaries. The pollutants I study include nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus, which when in excess contribute to noxious algae blooms in the lakes, and small plastic particles, which affect microorganisms, insects, and fish that sustain aquatic food webs. In particular, I’m interested in how those materials move through streams and rivers, and whether they can be broken down, processed, or retained in streams before they go downstream. This requires first determining the sources of nutrients and microplastic, then measuring the interactions with those materials and microorganisms active in decomposition, and then determining how far downstream the chemicals are transported and how they are incorporated into food webs.
Describe an experience you have had working with educators or the community. What was something that surprised you or that you especially enjoyed about the experience?
I was fortunate to spend a week on Lake Michigan aboard the research vessel Lake Guardian, with a group of teachers from throughout the Great Lakes. We collected samples from the surface water and sediment throughout the lake, and I walked the teachers through the process of isolating plastic particles, including digestions, filtration, and counting particles on the microscope. One of my favorite things about the experience was the enthusiasm that the teachers brought to topic, and how each of them used their own unique talents to come up with creative ways to explain our work in their classrooms. One of the teachers brought a video camera to interview me, detail the collection and counting processes, and give his students  and understanding of how and why we were doing this work. Another used video editing skills and a Go-Pro camera on the sampling equipment to put together fantastic videos of the devices we sent to the bottom of the lakes. This reinforced to me that teachers are at their best when they are using their talents, enthusiasm, and dedication to convey information in creative ways. I try to carry that spirit with me in my role as a teacher in the college classroom.
and understanding of how and why we were doing this work. Another used video editing skills and a Go-Pro camera on the sampling equipment to put together fantastic videos of the devices we sent to the bottom of the lakes. This reinforced to me that teachers are at their best when they are using their talents, enthusiasm, and dedication to convey information in creative ways. I try to carry that spirit with me in my role as a teacher in the college classroom.
Why do you think it is important for scientists to share their research with educators?
In my role as a scientist and teacher, I’ve added to my focus on my studies and students, by looking for more creative ways to share the mission of my work, which includes community service, speaking with students of all ages, and engaging the general public and teachers whenever possible. I’ve found the time spent doing this spreads the message of the research to a broader audience, and deepens my appreciation for the career I’ve developed. Speaking with educators like those on the research cruise on the Lake Guardian was one of the best ways for me to communicate in this way, as the teachers can take that information to their schools and classrooms.
What do you think are the most critical skills for students interested in a career in science?
Science requires a combination of lots of different skills. There are the obvious ones like attention to detail, curiosity about the natural world in all its forms, and the ability to think logically. One often overlooked ingredient for making a good scientist is an open mind with creative impulses. In order to make the step from one project to another, or the first step in a new project, a scientist has to come up with a new question to answer. This requires being interested in lots of different topics, being able to think about combining facts and ideas in new ways, and then creatively and carefully explaining those ideas to collaborators, funding sources, and students.
Contact Tim Hoellein at thoellein@luc.edu.
Illinois-Indiana Sea Grant is a part of University of Illinois Extension and Purdue Extension.
August 23rd, 2016 by IISG
“The site doesn’t glow!” assured Michigan Department of Environmental Quality (Michigan DEQ) geologist Sarah Pearson, to the relief of local teachers stepping foot on the land of what used to be the Zephyr oil refining facility in Muskegon, Michigan. The site is now home to a fertilizer company.
The 14 educators were taking part in a week-long West Michigan Great Lakes Stewardship Initiative that brought them to an area of wetlands that endured repeated oil spills during the decades prior to the 1990s that Zephyr was in business—refining, then switching to bulk storage.
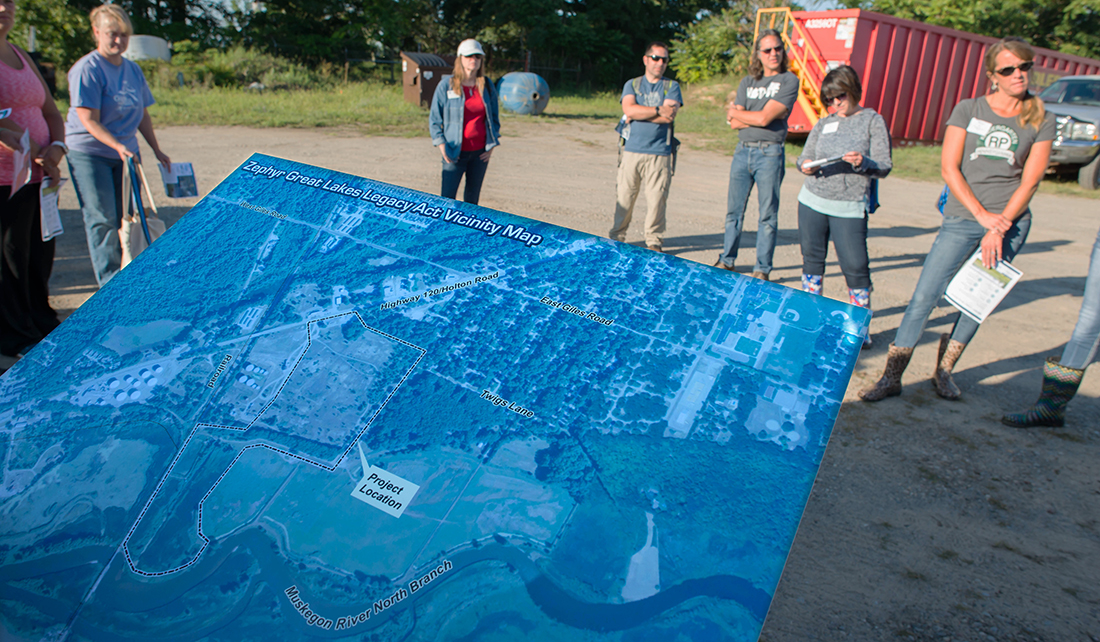

Teachers gather to look at a map of the Zephyr site.
Today there’s little visible indication of those frequent spills, which sometimes resulted in fires. Now and then you can still catch a whiff of oil or spot some sheen on the ground, but for the most part the landscape is picturesque.
The grasses are tall and the wildlife has started to return. But contamination, including petroleum products and heavy metals like lead and copper, remain just out of site in the sediment of Muskegon Lake.
“The funny thing is that you knew it existed, back in the day. But when we drove back there, you couldn’t see it. So it’s more out of sight, out of mind,” said Shannon Delora, Muskegon area transition coordinator for students in special education.
“Unless you are taken there, you don’t know all that’s happening, the good and the bad of it all.”
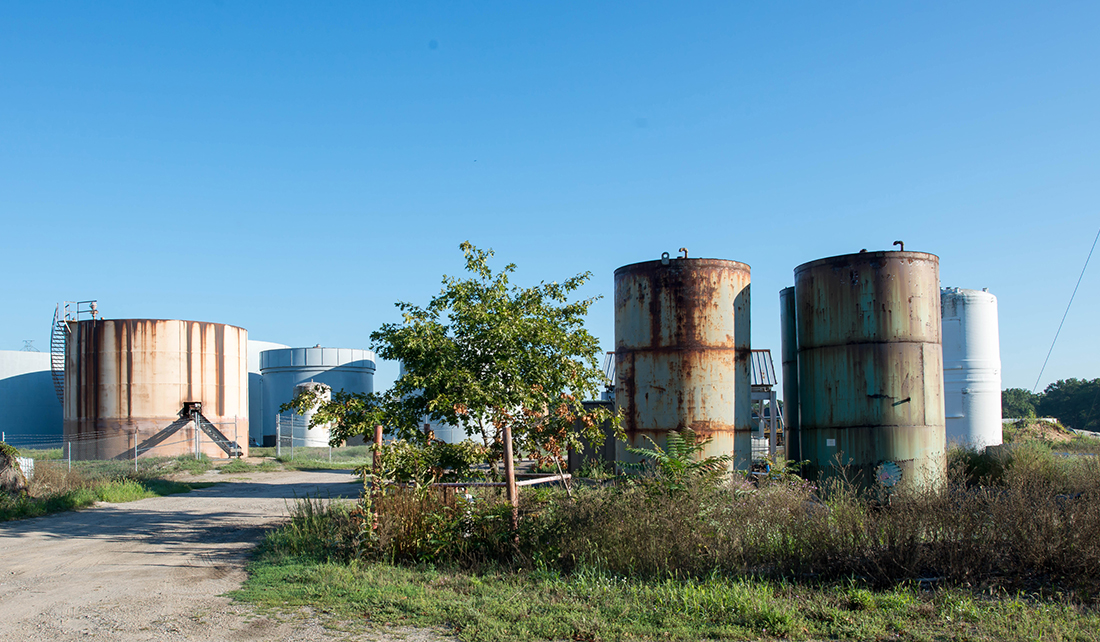

Tanks that at one time stored oil by Zephyr are now used by a fertilizer company that owns the land.
Ben Wegleitner, IISG social science outreach assistant, was on hand to introduce the latest version of Helping Hands, a curriculum that engages upper elementary and high school students in Great Lakes environmental stewardship. It is designed for schools located in Areas of Concern, like Zephyr, but can be applied to any Great Lakes community where large-scale environmental cleanup projects are ongoing.
The lessons touch on a variety of topics, like the effects of pollution and invasive species, and include hands-on activities.
 “If you need an opportunity to get your students out in the field and get involved in natural resources and pollution,” Wegleitner told the teachers, “there’s no shortage of opportunities to get your kids interested. Muskegon is a uniquely positioned area for that.”
“If you need an opportunity to get your students out in the field and get involved in natural resources and pollution,” Wegleitner told the teachers, “there’s no shortage of opportunities to get your kids interested. Muskegon is a uniquely positioned area for that.”
The Zephyr cleanup, which is funded through the Great Lakes Legacy Act, involves the U.S. EPA, Michigan DEQ, and IISG. The plan is to remediate 36,000 to 45,000 cubic yards, followed by habitat restoration. It’s slated to get started within the next six months and will take about a year and a half to complete.
“I was very unfamiliar with Zephyr,” said Beth Sipperley, a third grade teacher at Oak Ridge Elementary School.
“To go there and see it and to have the curriculum that really ties into it—one that’s so connected to Muskegon—is great.”
Illinois-Indiana Sea Grant is a part of University of Illinois Extension and Purdue Extension.
July 29th, 2016 by IISG
Listen to Kristin TePas’ radio interview with University of Illinois Extension’s Todd E. Gleason below.
Fifteen educators are once again on dry land recovering from a schedule just as packed as the Lake Guardian’s quarters. The 2016 Shipboard Science Workshop on Lake Superior aboard the U.S. EPA Great Lakes National Program Office research vessel wrapped up last week. The annual workshop was hosted by Center for Great Lake Literacy and led by Minnesota Sea Grant.
Using state-of-the-art sensors, the teachers, alongside four research scientists from Minnesota and U.S. EPA, took part in water sampling—all day and night—to evaluate the presence of zooplankton, aquatic invasive species, and water quality and nutrient differences over time.

Teachers working in the lab on the Lake Guardian.
The teachers analyzed the samples in on-board laboratories and presented their findings after the ship dropped anchor. But their work is just beginning. The teachers now have the task of inspiring their own students to become Great Lakes scientific explorers.
“So many of our labs we do in class, the students have to do an experiment that simulates what would happen in real life,” Ashlee Giordano a science teacher at Northfield Jr./Sr. High School in Wabash, Indiana. “It is meaningful, however, showing students what I did, and the data we collected would really hit home for them.”
This year’s cruise received some special attention from University of Illinois Extension’s radio personality Todd E. Gleason who interviewed IISG community outreach specialist and liaison to U.S. EPA Kristin TePas over the phone while she was still on the trip. The interview was aired on stations throughout Illinois.
“We really want them to be more comfortable with science and understanding the process of research,” TePas said.

This year the teachers hailed from seven Great Lakes states. Two were from Illinois and one from Indiana.
The exhaustive effort scientists go through was not lost on Cheryl Dudeck, a biology and human anatomy teacher at King College Prep High School in Chicago.
“I was surprised by how many people it takes to complete one week of research. I also was surprised to find out that the research happens 24/7 and how it changes with the weather conditions,” Dudeck said.
“I think that most people do not understand the importance and complexity of the Great Lakes.”
Illinois-Indiana Sea Grant is a part of University of Illinois Extension and Purdue University Extension.
June 24th, 2016 by IISG
U.S. EPA’s Research Vessel Lake Guardian graces our page once again for this year’s annual Shipboard Science Workshop. “This workshop allows educators to work on a research project with a Great Lakes scientist for the week they are on the ship,” said IISG Educator Allison Neubauer. “They use equipment to collect samples from the lake, analyze them in the labs onboard the ship, and come up with answers to the questions of their particular research project.”
Past workshops have included collecting data on plankton communities, plastic pollution, and overall water quality of the Great Lakes. This season, educators aboard the R/V Lake Guardian will have the opportunity to participate in what is known as The Incredible Shrinking Cup Lab, coordinated by Kristin TePas, IISG’s community outreach specialist.

The principle guiding The Incredible Shrinking Cup Lab is called Boyle’s law, which, when simplified, says that the volume of a gas is inversely proportional to the pressure being exerted upon it. We see this with weather balloons, which, when they’re launched, can range from 2.5 ft. to 8 ft. in diameter, but expand more than four times in diameter during flight, becoming as large as 32 ft. wide. As a balloon gains altitude, less pressure is being exerted on it from the outside, allowing the gas inside to expand until, ultimately, the balloon pops.
The Incredible Shrinking Cup Lab takes things in the opposite direction, observing the effects of increased pressure as Styrofoam cups are sunk hundreds of feet underneath the water. Gas pockets inside the Styrofoam cups shrink as the distance below sea level, and subsequent pressure, increases, compressing the cup’s structure, making it smaller.
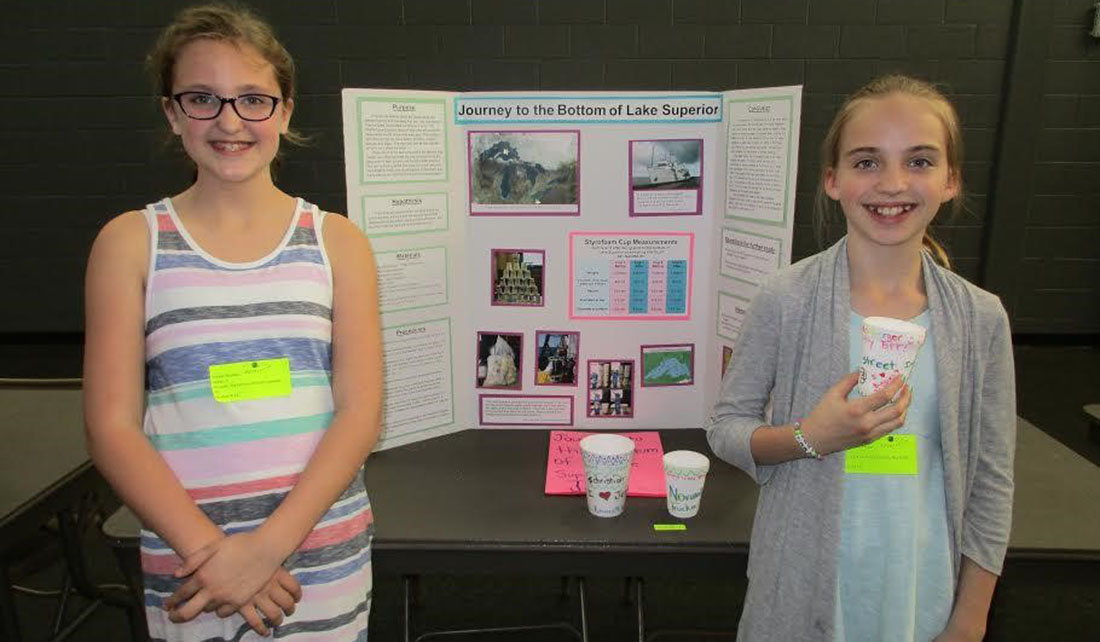

Two students of Marcy Burns, Main Street Intermediate School in Norwalk, Ohio, pose after winning third place in the OhioView SATELLITES Conference and research project fair at the University of Toledo.
This activity provides students the opportunity to see the effects of Boyle’s law first hand. Before the cups are submerged, students are taught how to measure their volume, density, and mass. They personalize their cups to know whose is whose, craft hypotheses on what will happen to the cups, and are put into direct contact with research scientists, who do the submerging themselves once at their stations in the ocean or in the Great Lakes. Allison Neubauer was able to document two rounds of sending down cups this past April while aboard the R/V Lake Guardian in Lake Superior.
Illinois-Indiana Sea Grant is a part of University of Illinois Extension and Purdue Extension.
January 14th, 2015 by iisg_superadmin
A closer look at web tools and sites that boost research and empower Great Lakes communities to secure a healthy environment and economy.
.png) Educators interested in strengthening aquatic science programs and encouraging Great Lakes stewardship—look no further than the new Center for Great Lakes Literacy (CGLL) website.
Educators interested in strengthening aquatic science programs and encouraging Great Lakes stewardship—look no further than the new Center for Great Lakes Literacy (CGLL) website.
Created by Sea Grant educators throughout the region, the site is a one-stop-shop for classroom activities designed to boost Great Lakes literacy. Educators will find information on and links to teacher-tested curriculum like Fresh and Salt and Estuaries 101. And the Teacher Feature allows visitors to hear about education success stories directly from colleagues across the region.
Visitors to the site can also learn about the latest professional development opportunities available throughout the region. For example, teachers interested in the annual Shipboard Science Workshop, held this year on Lake Michigan, can find workshop information and application deadlines. Featured blogs also make it possible to read about teacher experiences at past CGLL workshops and follow along with the latest projects.
For more information on upcoming educator workshops and available curriculum, contact Terri Hallesy.
January 13th, 2015 by iisg_superadmin
Real-world, hands-on activities are bringing Great Lakes science alive for a group of Wisconsin middle school students. Our friends at Wisconsin Sea Grant have the story.
Two Wisconsin teachers have made exceptional use of the educational resources that Sea Grant has to offer. And not just resources from Wisconsin Sea Grant—the teachers have found valuable support from the Center for Great Lakes Literacy, a collaborative effort by educators in the Great Lakes Sea Grant Network funded through the Great Lakes Restoration Initiative.
The teachers are Lynn Kurth and Cindy Byers. Kurth works as a science teacher for Prairie River Middle School in Merrill, Wis. Just a 50-minute drive away, Byers works as a science and reading teacher for Rosholt Middle School in Rosholt, Wis.
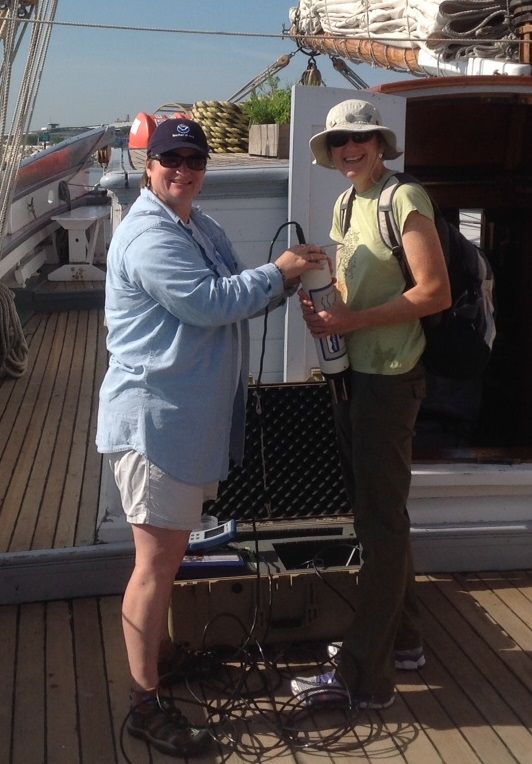
They met in 2011 during a week-long voyage on the Lake Guardian, a research vessel owned by the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). They were participating in a Shipboard and Shoreline Science Workshop, a program conducted by the Great Lakes Sea Grant programs through the former Centers for Ocean Sciences Education Excellence (which has become the Center for Great Lakes Literacy). They were part of a team of five colleagues who worked on a research project together. Kurth and Byers bonded over a Hydrolab—a large, tubular piece of water testing equipment—and it’s led to bigger and better things for both them, their students, and other teachers across the country.
The Hydrolab takes various water quality readings. Kurth and Byers were drawn to it because both of their schools are near rivers and the EPA was providing the device on loan for use with their classrooms after the cruise. They saw the opportunity to partner in the future.
It worked. “We supported each other’s teaching and enriched each other’s classrooms by having this collaboration,” Byers said. “We had the kids Skype with each other a couple of times and present the Hydrolab data they collected. Even though our schools are not that far apart, it seemed quite exotic to the kids and they were excited to use a piece of equipment that scientists use. A lot of the reasons we’ve been able to do so much with the program is that we’ve been supporting each other all along.”nce-in-a-lifetime learning experiences for students. In fact, 26 classes across the Great Lakes region took a break from their regular activities over the last year to video chat with the scientists behind the EPA Lake Guardian‘s annual monitoring cruises. Some students even took a guided virtual tour of the boat.
And now a new group of teachers and non-formal educators have an opportunity to work with Sea Grant specialists to introduce activities like these into their aquatic sciences sections during the 2015 Shipboard Science Workshop on Lake Michigan. Applications for the 15 available spaces are due February 10.
September 25th, 2014 by iisg_superadmin
 Charleston, IL may be hundreds of miles from where the R/V Lake Guardian was collecting samples in Lake Erie earlier this week, but that didn’t stop a group of sixth graders from taking a tour of the U.S. EPA vessel. From the comfort of their classroom, more than 60 students and teachers watched as EPA researcher Beth Hinchey Malloy talked about living and working on a boat and showed them around.
Charleston, IL may be hundreds of miles from where the R/V Lake Guardian was collecting samples in Lake Erie earlier this week, but that didn’t stop a group of sixth graders from taking a tour of the U.S. EPA vessel. From the comfort of their classroom, more than 60 students and teachers watched as EPA researcher Beth Hinchey Malloy talked about living and working on a boat and showed them around.
 The tour started, of course, on the ship’s deck and quickly moved inside to the labs, where scientists took a break from processing samples to explain how studying bug populations helps researchers judge the health of aquatic ecosystems. From there it was on to the galley to see what’s for lunch and up to the bridge to chat with the captain.
The tour started, of course, on the ship’s deck and quickly moved inside to the labs, where scientists took a break from processing samples to explain how studying bug populations helps researchers judge the health of aquatic ecosystems. From there it was on to the galley to see what’s for lunch and up to the bridge to chat with the captain.

And the students had more than a few questions, particularly for the captain—Is it easy to drive the boat? How can you tell how deep the water is? Where does the Lake Guardian go?
Students also got a sneak peak at the type of equipment they will use later this year to collect data on water characteristics like dissolved oxygen, conductivity, and pH. Their teacher, Pamela Evans, is one of several scheduled to use the Hydrolab to make science class more hands-on this year.
The event ended after a jam-packed 30 minutes because another class was waiting on deck to take the tour. In fact, eight classes across the Great Lakes region got a first-hand look at the Lake Guardian this week. And this is just the beginning. The research vessel will soon dock for the winter, but video chats with EPA scientists will continue throughout the school year.
The video chats and equipment loan program are all part of efforts by IISG and the EPA Great Lakes National Program Office to boost Great Lakes education. Teachers were introduced to the programs, along with other classroom resources, during the annual Shipboard Science workshop.


 and understanding of how and why we were doing this work. Another used video editing skills and a Go-Pro camera on the sampling equipment to put together fantastic videos of the devices we sent to the bottom of the lakes. This reinforced to me that teachers are at their best when they are using their talents, enthusiasm, and dedication to convey information in creative ways. I try to carry that spirit with me in my role as a teacher in the college classroom.
and understanding of how and why we were doing this work. Another used video editing skills and a Go-Pro camera on the sampling equipment to put together fantastic videos of the devices we sent to the bottom of the lakes. This reinforced to me that teachers are at their best when they are using their talents, enthusiasm, and dedication to convey information in creative ways. I try to carry that spirit with me in my role as a teacher in the college classroom.





.png)
.jpg)



