August 19th, 2014 by iisg_superadmin
Our summer internship program has wrapped up for another year. This year, seven students and recent graduates worked with our specialists on a broad range of issues, including AIS prevention, sediment remediation, and water supply planning. Erika Lower and Mark Krupa spent their internship working with Caitie McCoy, IISG’s social scientist.
“We did a little bit of everything this summer—from compiling reports on public perceptions of river cleanups in Detroit and Milwaukee to conducting interviews with community members to covering a day of outreach at Indiana’s Roxana Marsh” said Erika, a graduate from Virginia Tech who also interned last year with Virginia Sea Grant. “Working on so many diverse projects mean there was rarely a slow day at the office.”
Their favorite experiences came while onsite at Great Lakes Legacy Act sediment remediation projects. One such trip took them to the Upper Trenton Channel near Detroit to conduct a needs assessment that will help the project team tailor outreach products and messaging to those who use and visit the river.
“Our Detroit trip was definitely my favorite part,” said Mark, a University of Illinois alum. “We talked to over 30 different community members. It was great to see the site we had researched and really get to know the community, their concerns, and how they value the waterway.”
“How often do you get a chance to tour the site of a former oil refinery or conduct an interview from a powerboat in the middle of the Detroit River while watching the sun rise?” Erika added.
 These experiences further boosted their interest in the social science and highlighted its importance in environmental conservation.
These experiences further boosted their interest in the social science and highlighted its importance in environmental conservation.
“I’ve always been interested in the human dimensions of environmental science, but actually getting out into the field and talking with community members about their hopes and concerns illustrated just how complex finding the best solution to environmental issues can be,” said Erika.
“Before this internship, I didn’t realize how important it is to address local perceptions and concerns surrounding environmental cleanup projects,” said Mark. “Also, I hadn’t realized how much thought goes into designing outreach materials in order to ensure they attract an audience and effectively communicate the message.”
With their internship complete, Erika and Mark are turning their attention to graduate school. Mark will begin a Master’s in public health at Saint Louis University later this month. And Erika plans to complete graduate work in science communication or environmental social science.
July 28th, 2014 by iisg_superadmin
 Scientists and engineers are working together to design a clean-up plan for Michigan’s Upper Trenton Channel, where high concentrations of historic pollutants pose a threat to aquatic life and public health. The process began about a year ago with a feasibility study. In January, local residents had a chance to weigh-in on an early draft of the plan. And in the coming years, this Great Lakes Legacy Act project could remove or cap around 240,000 cubic yards of contaminated sediment.
Scientists and engineers are working together to design a clean-up plan for Michigan’s Upper Trenton Channel, where high concentrations of historic pollutants pose a threat to aquatic life and public health. The process began about a year ago with a feasibility study. In January, local residents had a chance to weigh-in on an early draft of the plan. And in the coming years, this Great Lakes Legacy Act project could remove or cap around 240,000 cubic yards of contaminated sediment.
Just as important as the clean-up effort itself, is ensuring that local communities and other key stakeholders understand the project and its goals. But before they can begin public outreach, project partners have to understand and appreciate the role the channel and nearby Detroit River play in the communities.
 That is where IISG’s social scientist Caitie McCoy and her interns Erika Lower and Mark Krupa come in. The three were in Michigan earlier this month to conduct a needs assessment that will help the project team tailor outreach products and messaging to those who use and visit the river.
That is where IISG’s social scientist Caitie McCoy and her interns Erika Lower and Mark Krupa come in. The three were in Michigan earlier this month to conduct a needs assessment that will help the project team tailor outreach products and messaging to those who use and visit the river.
They interviewed around 35 people with diverse backgrounds—everyone from area residents to city planners to members of boating associations—to learn more about their perceptions of the channel and river. The final results of the study won’t be available for a few months, but the interviews have already given Caitie, Erika, and Mark a better understanding of the interests and concerns surrounding this popular recreation site.
“One interesting thing we learned was that the safety of the channel and river during dredging is of prime importance to the community,” said Caitie. “This is a fast flowing channel, and we will need to explain the science and engineering behind what keeps stirred up sediment from flowing downstream during the project—in terms that everyone can understand.”
 An impromptu trip on the channel also gave Caitie, Erika, and Mark deeper insight into how the community uses the channel and river. The trip—which set off bright and early on the 16th—was led by the Wyandotte Rowing Club. Later that night, the group took to the water once again with one of the residents they interviewed.
An impromptu trip on the channel also gave Caitie, Erika, and Mark deeper insight into how the community uses the channel and river. The trip—which set off bright and early on the 16th—was led by the Wyandotte Rowing Club. Later that night, the group took to the water once again with one of the residents they interviewed.
Similar studies for the Sheboygan River and St. Louis River Areas of Concern have already helped shape outreach efforts there and allowed project partners to gauge changes in community perceptions at the end of a clean-up project.
The Upper Trenton Channel, which sits about 20 miles south of Detroit, is part of the Detroit River AOC. Project partners include Michigan Sea Grant, Friends of the Detroit River, the Detroit River Public Advisory Council, the Michigan Department of Environmental Quality, the Michigan Department of Community Health, and the U.S. EPA.
June 27th, 2014 by iisg_superadmin
Last month, IISG’s Caitie McCoy held a workshop for teachers in the Buffalo River area of New York to debut a new curriculum, “Helping Hands: Restoration for Healthy Habitats.” This latest edition is specific to the Buffalo River area of concern, and offers a direct link to important environmental projects that are taking place in the students’ community.
 The Great Lakes Legacy Act remediation project on the Buffalo River resumed June 16, and will remove 500,000 cubic yards of contaminated sediment from the river, then replace native aquatic plants to help restore the local ecosystem.
The Great Lakes Legacy Act remediation project on the Buffalo River resumed June 16, and will remove 500,000 cubic yards of contaminated sediment from the river, then replace native aquatic plants to help restore the local ecosystem.
18 teachers from grades 4-11 attended the workshop to learn more about the restoration project and the curriculum, and were treated to hands-on activities and a tour of the river area to help bring the project and its impacts into their classes.
 “It’s great to see so many educators come out to this kind of workshop,” Caitie said. “Many teachers want to incorporate place-based learning in their science curriculum, but may lack resources to do so. Now instead of using distant examples like rainforests to teach science, they can use their neighborhood rivers and lakes. These are places that students can visit and experience the science in person. They develop a love for these places and want to protect them.”
“It’s great to see so many educators come out to this kind of workshop,” Caitie said. “Many teachers want to incorporate place-based learning in their science curriculum, but may lack resources to do so. Now instead of using distant examples like rainforests to teach science, they can use their neighborhood rivers and lakes. These are places that students can visit and experience the science in person. They develop a love for these places and want to protect them.”
June 20th, 2014 by iisg_superadmin
Two years ago, a group of middle school students planted native seedlings along the banks of Roxana Marsh to celebrate the successful cleanup of the waterway. On Monday, those same students returned for another day of learning and service to find the marsh in bloom – thanks in large part to their efforts.
“It’s good to know that we did something phenomenal to help our environment,” said Sandra Olivarria, one of the East Chicago Lighthouse Charter School students participating in the event.
Monday morning’s stewardship began with speeches from state and local officials, including Indiana Representative Earl Harris, Senator Lonnie Randolph, and Mayor Anthony Copeland of East Chicago.
“We need to start to get everyone involved in this kind of project at an early age so that when you grow up, you become part of something that keeps you involved for the long term,” Representative Harris said.
 The rest of the day was devoted to hands-on activities that encouraged students to get familiar with the plants and animals inhabiting the area. The class looked at native and non-native plant species growing around the marsh, then checked on the flowers they had originally sprouted in their classroom. The kids worked together to pull up the invasive clover that had grown around their plantings – a little tricky at times, they said, but “pretty fun, too.”
The rest of the day was devoted to hands-on activities that encouraged students to get familiar with the plants and animals inhabiting the area. The class looked at native and non-native plant species growing around the marsh, then checked on the flowers they had originally sprouted in their classroom. The kids worked together to pull up the invasive clover that had grown around their plantings – a little tricky at times, they said, but “pretty fun, too.”
“It feels so good to come back and see what we did two years ago, and see it all grown and restored!” one student exclaimed.
 Down by the water, volunteer scientists helped students take samples of mud from the marsh to collect bottom-feeding aquatic animals that lived there. The students identified various species of worms, snails, larvae, and tadpoles, and were delighted at the chance to handle these small creatures.
Down by the water, volunteer scientists helped students take samples of mud from the marsh to collect bottom-feeding aquatic animals that lived there. The students identified various species of worms, snails, larvae, and tadpoles, and were delighted at the chance to handle these small creatures.
The class also cleaned up trash from the marsh and along Roxana Drive, helping to beautify the area.
“I’m really proud of all the work the students performed today,” said IISG environmental social scientist Caitie McCoy. “It was thrilling to have them come back and take care of a beautiful environment that they helped create. Today, nature was our classroom, and I think the students learned a lot.”
Roxana Marsh is now home to blue herons, wild irises, and all sorts of aquatic life. But it wasn’t always that way. Located on the Grand Calumet River, the marsh was heavily polluted for more than a century with byproducts of heavy industry around East Chicago. Federal and state agencies worked to dredge the river, removing contaminated sediment and restoring the surrounding habitat as part of the U.S. EPA’s Great Lakes Legacy Act.
 Monday’s restoration activities and press event brought together partners from the US EPA Great Lakes National Program Office, US Fish and Wildlife, Indiana Department of Environmental Management, Indiana Department of Natural Resources, Illinois-Indiana Sea Grant, The Nature Conservancy, and Shirley Heinz Land Trust. The Roxana Marsh cleanup and Caitie’s work to improve community engagement here and at other Areas of Concern is possible because of the Great Lakes Restoration Initiative and the Great Lakes Legacy Act.
Monday’s restoration activities and press event brought together partners from the US EPA Great Lakes National Program Office, US Fish and Wildlife, Indiana Department of Environmental Management, Indiana Department of Natural Resources, Illinois-Indiana Sea Grant, The Nature Conservancy, and Shirley Heinz Land Trust. The Roxana Marsh cleanup and Caitie’s work to improve community engagement here and at other Areas of Concern is possible because of the Great Lakes Restoration Initiative and the Great Lakes Legacy Act.
Teachers interested in integrating AOC issues into their classroom can find activities and other resources in our Helping Hands curriculum.
January 16th, 2014 by Irene Miles
The future is looking bright for the Grand Calumet River. Completed and ongoing restoration projects along the heavily industrialized river have already removed or capped more than 2 million pounds of sediment ridden with toxins like PCBs and heavy metals. And late last year, the EPA took the first step towards cleaning up the final sections of river yet to be addressed.
 It will be a long road to restoration, but this step means those who live and work nearby can expect to see a clean river bottom with a vibrant plant community as early as 2024.
It will be a long road to restoration, but this step means those who live and work nearby can expect to see a clean river bottom with a vibrant plant community as early as 2024.
“This means a lot to the community,” said Caitie McCoy, IISG’s environmental social scientist. “I was recently at a meeting with community members in northwest Indiana who have been fighting for this river for over 50 years where the EPA announced their plans. Their reaction was almost a mixture of joy and disbelief. When you devote your whole life to something, making baby steps of progress along the way, it must be surreal to finally reach that moment. It is an honor to be a part of it.”
For now, efforts are focused on determining the feasibility of cleaning up four river segments: one in Gary, IN and three more in East Chicago, IN, where there is also funding to design a tailored cleanup plan.
Remediation projects are big undertakings. One common strategy, for example, requires contaminated sediment to be dredged, pumped to shore, dried, and trucked off to fill sites certified to handle this kind of waste. At the same time, the water pulled out during dredging has to be treated before it can be returned to the river.
To ensure the success of any new projects in these areas, the EPA is teaming up with the East Chicago Water Management District, the Gary Sanitary District and other local partners to take a closer look at restoration needs. In Gary, planning will likely be completed sometime this year, but it will be another year still before the group announces plans for the stretch flowing through East Chicago. Before any actual cleanup work can begin, though, additional funding and partners will be needed for both projects.
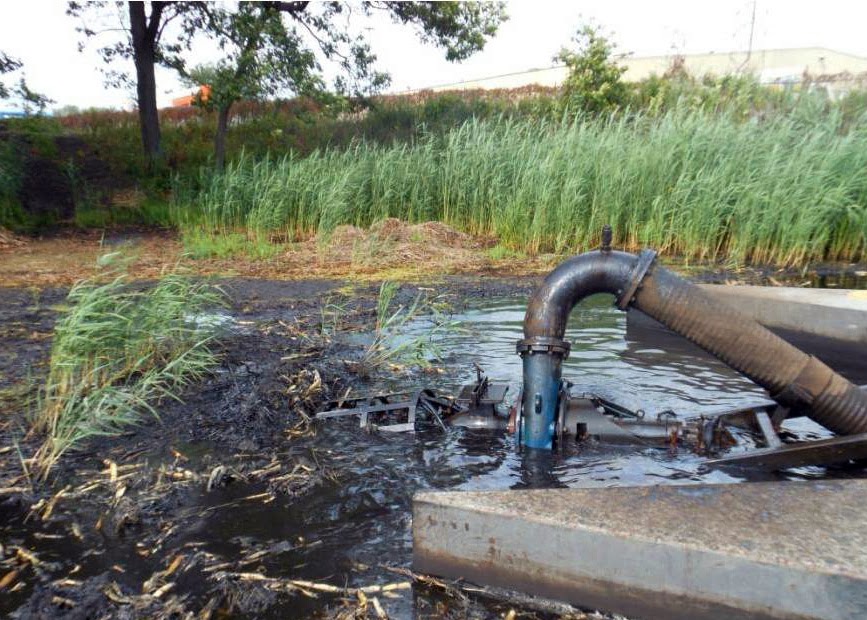 The next few years will also prove significant for two other sections of river. Cleanup efforts at the river’s westernmost end in Hammond, IN are expected to kick off this year. And work on a larger segment of the river just a few miles to the east is expected to wrap up in 2015. There, construction crews have already removed much of the contaminated sediment along the river bed and are now turning their sights to nearby wetlands. Project partners have also begun removing invasive plants along this stretch to make room for native species that will be planted in 2015.
The next few years will also prove significant for two other sections of river. Cleanup efforts at the river’s westernmost end in Hammond, IN are expected to kick off this year. And work on a larger segment of the river just a few miles to the east is expected to wrap up in 2015. There, construction crews have already removed much of the contaminated sediment along the river bed and are now turning their sights to nearby wetlands. Project partners have also begun removing invasive plants along this stretch to make room for native species that will be planted in 2015.
Efforts to restore the Grand Calumet River are part of the Great Lakes Legacy Act, the Great Lakes Restoration Initiative, and the Resource Conservation and Recovery Act.
*Photo 1 courtesy of Lloyd DeGrane
*Photo 2 courtesy of U.S. EPA
December 17th, 2013 by Irene Miles
Residents of Sheboygan, Wisconsin are seeing their namesake river, and the opportunities it holds for the community, in a whole new light thanks to a suite of cleanup projects completed in 2012 and 2013. For decades, high concentrations of PCBs and other industrial pollutants lining the riverbed had kept river-goers and businesses at arm’s length. But with the contaminated sediment removed and habitat restoration well underway, the public is embracing the river with full force.
 “After nearly three decades of being a black eye of the community, we are thrilled that the Sheboygan River and harbor is being restored to reduce health risks to people, fish, and wildlife, and will greatly enhance opportunities for economic development,” said Adam Payne, Sheboygan County Administrator at a 2012 press event celebrating the project.
“After nearly three decades of being a black eye of the community, we are thrilled that the Sheboygan River and harbor is being restored to reduce health risks to people, fish, and wildlife, and will greatly enhance opportunities for economic development,” said Adam Payne, Sheboygan County Administrator at a 2012 press event celebrating the project.
Perhaps the biggest boost so far has been to recreation. Dredging the equivalent of 15,000 dump trucks of contaminated sediment left boaters and anglers with a deeper river that is easier to access and navigate. With the contamination gone, the community has also started to see the Sheboygan River as a safe place to spend an afternoon. Just a few months after the project ended, residents reported seeing more and bigger boats navigating in and out of the river’s harbor, and they expect to see even more fishing and boating in the coming years.
“Anytime you have a healthy river going through a community, you have a better quality of life,” said one resident to IISG’s Caitie McCoy and Emily Anderson as part of a series of interviews about how community perceptions of the river had changed.
The deeper, cleaner river has also attracted local businesses. Everything from coffee shops to digital communications companies have opened along the river, and more businesses are expected to follow. It is too early to say just how much the cleanup project will impact things like property values, tourism, and redevelopment, but it is already clear that riverfront development is on the rise thanks to changes to the river and its newly restored status within the community.
“When it comes right down to it, those who would invest in the river and want to develop this property, they are really after the water access,” said another resident.
 There is good news for local wildlife too. With the dredging work completed, the Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources and other project partners have begun work to restore native habitats. Recently planted native plants have caught the attention of a variety of species, including cranes and blue birds. With this work done, the Sheboygan River will officially be taken off the list of most polluted places in the Great Lakes.
There is good news for local wildlife too. With the dredging work completed, the Wisconsin Department of Natural Resources and other project partners have begun work to restore native habitats. Recently planted native plants have caught the attention of a variety of species, including cranes and blue birds. With this work done, the Sheboygan River will officially be taken off the list of most polluted places in the Great Lakes.
October 7th, 2013 by Irene Miles
Among the many Areas of Concern (AOCs) designated by the International Joint Commission, Illinois-Indiana Sea Grant has been involved in several providing research and reports on local stakeholders perceptions of cleanup operations and ways in which they are affected by the projects. This latest report details the St. Louis River AOC.
From IISG’s Caitie McCoy:
“A report on stakeholder perceptions of the St Louis River Area of Concern (AOC) and attitudes toward the cleanup and restoration work is now available. This summer, I traveled to the St Louis River with my intern Emily Anderson to perform social science research on community attitudes toward remediation and restoration. The river is located on the border between Duluth, MN and Superior, WI, and is the largest U.S. AOC. The report will help tailor efforts of the Spirit Lake Outreach Team toward local stakeholder needs and interests at the current Great Lakes Legacy Act site in the river, Spirit Lake.
Emily provided her thoughts on the experience – ‘Being part of the research team for this project allowed me to experience firsthand how social science contributes to environmental remediation and restoration. Conducting the interviews with Caitie, I met so many intriguing and knowledgeable people; I now see the direct implications that stakeholder input can have for both outreach and project design.’
This assessment is part of a larger effort to understand how AOC work influences stakeholder perceptions and use of waterways at a regional scale. A similar report on the Sheboygan River is available and a follow-up report on Sheboygan, post-cleanup, is coming soon.”
July 2nd, 2013 by Irene Miles
The Great Lakes Ecological and Economic Protection Act was introduced by Senators Carl Levin (D-MI) and Mark Kirk (R-IL), co-chairs of the Senate Great Lakes Task Force, along with Senators Debbie Stabenow (D-MI), Amy Klobuchar (D-MN), Sherrod Brown (D-OH), Richard Durbin (D-IL), Al Franken (D-MN), Charles Schumer (D-NY) and Tammy Baldwin (D-WI).
 In addition to reauthorizing the Great Lakes Legacy Act, which provides support for communities to clean up waterways that are designated Areas of Concern (AOC) the United States and Canada, the new legislation would continue funding the Great Lakes Restoration Initiative and the EPA Great Lakes National Program Office.
In addition to reauthorizing the Great Lakes Legacy Act, which provides support for communities to clean up waterways that are designated Areas of Concern (AOC) the United States and Canada, the new legislation would continue funding the Great Lakes Restoration Initiative and the EPA Great Lakes National Program Office.
The 10-minute video, produced by Illinois-Indiana Sea Grant and Wisconsin Sea Grant, explores Great Lakes waterways blighted by decades of industrial discharges like heavy metals, oil, and chemicals such as PCBs and PAHs. The 2002 Great Lakes Legacy Act created an initiative to clean up contamination in these AOCs. There are currently 29 AOCs in the United States. The habitat, water, and sediment quality have become severely degraded at these sites.
The video informs anglers, boaters, residents, and local businesses of the benefits that can come from a remediated AOC through the Legacy Act. The procedures and successes are the result of strong partnerships among states, municipalities, non-governmental organizations and businesses. Under this voluntary, collaborative program, the EPA and its non-federal partners have allocated almost $400 million toward sediment remediation.
As of September 2012, the program has removed or capped 2.1 million cubic yards of degraded sediment. But more waterways need to be cleaned up, and community involvement is essential.
Learn more about the Great Lakes Legacy Act at the EPA’s GLLA webpage.
May 29th, 2013 by Irene Miles
Revitalizing Local Waterfront Economies: The Great Lakes Legacy Act is a new video that welcomes people and partners to the benefits of restoring degraded rivers, harbors, and lakes.
Before modern-day environmental regulations, Great Lakes waterways became blighted by decades of industrial discharges. The Legacy Act was established in 2002 to clean up contamination in these places, known as Areas of Concern. The Legacy Act is helping to revitalize local waterfront economies through strong partnerships with states, municipalities, and businesses.
Altogether, the Legacy program has removed or capped 2.4 million cubic yards of sediment. But more waterways need to be cleaned up, and community involvement is essential. “This video can help simplify and personalize the sediment cleanup process, which at first glance may seem too complex and scientific,” said Caitie McCoy, IISG environmental social scientist. “The Great Lakes Legacy Act has been incorporating community values with technical science for more than a decade.
“Cleaner lakes and rivers improve human health, fish and wildlife health, recreation, tourism, and redevelopment so that residents can better capitalize on these opportunities,” added McCoy.
The 10-minute video was produced by IISG and Wisconsin Sea Grant with funding from U.S. EPA Great Lakes Restoration Initiative. You can view the video online here or at the Illinois-Indiana Sea Grant YouTube channel.
 These experiences further boosted their interest in the social science and highlighted its importance in environmental conservation.
These experiences further boosted their interest in the social science and highlighted its importance in environmental conservation. 










