June 22nd, 2017 by IISG
Unfortunately in the United States we pollute at a rate much faster than we can put control measures in place. New chemicals and substances are continually being developed and used to enhance our industrial processes and products. A drawback to this advancement is that in some cases, when a chemical so novel, we have difficulty understanding the full effects it’s having on the environment or public health. This is what researchers are looking into when they study emerging contaminants.
As part of the IISG pollution prevention team led by Sarah Zack, I attended the Emerging Contaminants in the Aquatic Environment Conference (ECAEC), organized by the Illinois Sustainable Technology Center and IISG. The conference was a two-day crash course on the newest pollutants causing concern for the health of our waterways. Nearly 100 people attended to listen to four invited speakers, 27 contributed talks, and view 18 posters.

While last year’s conference zeroed in on contamination from pharmaceuticals and personal care products, this year we heard from researchers studying a wide variety of contaminants—from harsh-sounding chemicals used for things like flame retardants and stain repellents, to everyday items winding up as litter and microplastic on our beaches.
I found it reassuring to hear from researchers who are working so diligently to understand how these contaminants are getting into our water, how they move through the ecosystem, and their effects on not only the tiniest organisms in the environment, like microscopic plankton but all the way up to humans as well.
One of the four keynote speakers, Barbara Mahler from the U.S. Geological Survey, presented her research on coal-tar-based pavement sealcoat that is sprayed or painted on top of many asphalt parking lots, driveways, and playgrounds. Mahler found that coal-tar sealcoat, and particularly the dust that results from its wear and tear, is a major source of polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) contamination. Many PAHs are known to cause cancer, mutations, and birth defects in addition to being acutely toxic to aquatic life. Her work has informed policy in Austin, Texas where she conducted her research, as well as in other states and cities across the country.
Another keynote and familiar face for Illinois-Indiana Sea Granters, Tim Hoellein discussed several projects he’s working on relating to anthropogenic litter—trash that is making its way from people onto our beaches, in our rivers, and ending up in our Great Lakes.
And it’s not just the chemists and biologists who are toiling away on this complex, moving-target-of-an-issue. Having been to my share of scientific conferences, I was impressed at the variety of disciplines represented at ECAEC. Social scientists, educators, and even an attorney (yet another captivating keynote speaker, Stephanie Showalter Otts) also weighed in on the conversation of how to tackle the problem of emerging contaminants.
For me, it was especially cool to hear scientists in the room call out the necessity of working across disciplines and involving social scientists to further the reach of their research. It’s clear that the road ahead will not be easy, but I walked away from this conference feeling encouraged that there are brilliant, innovative people who are working to address these challenges from many angles.
Illinois-Indiana Sea Grant is a part of University of Illinois Extension and Purdue University Extension.
April 6th, 2016 by IISG
The Pharmaceuticals and Personal Care Products (PPCPs) in the Environment conference at the I Hotel in Champaign, Illinois on Monday welcomed dozens of researchers, officials, academics, and high school students. The 10 students from Pontiac High School in Illinois understood very well the hazards PPCPs pose to the health of people and the environment.
That’s not at all surprising because they are part of the P2D2 (Pontiac Prescription Drug Disposal) program created by their teacher 45-year-old Paul Ritter who’s been teaching for 22 years. Ritter developed the program nine years ago after failing to come up with an answer to his wife’s question about what to do with some unwanted medication they had in their home.
The purpose of P2D2 is to provide communities with a proper method of pharmaceutical disposal that effectively reduces the misuse and abuse of pharmaceuticals as well as improves water quality.
Since 2007 Ritter can boast the program’s success not just in the United States, but in six additional countries. Millions of pounds have of medicine have been properly disposed of and laws have been enacted to prevent medications from getting into the environment and into the wrong hands through the use of P2D2.
“My students help perpetuate the national model—they established the national model,” Ritter declared at the conference.
Senior Jacob Jiles who took the class with Ritter just to get another science credit knows he got much more out of the experience than he was expecting.
“Cumulatively with the program we’ve eradicated 3 million pounds of pharmaceuticals, so that means 3 million pounds that have been taken out of the streets and or the water system,” Jiles said.
“That’s kind of reassuring that we’ve done that.”
IISG in conjunction with the Illinois Sustainable Technology Center organized the conference with funding from University of Illinois Extension.
November 5th, 2015 by iisg_superadmin
A new version of the award-winning curriculum The Medicine Chest is now available! This updated and revised version includes new lessons and new teaching approaches. Here’s the story of how this edition came to be.
In 2012, I started in a new position at the University of Illinois and was introduced to the issue of pharmaceuticals and personal care product (PPCP) pollution. I thought it was fascinating and realized that past instructions to flush medicine down the toilet probably weren’t based on research.
I was interested even then in developing a curriculum on this emerging issue, but it wasn’t until I joined IISG that an opportunity materialized. It was then that I came to learn about the compendium of lessons known as The Medicine Chest that includes wonderful place-based stewardship lessons. I felt I could enhance the content by emphasizing the “Why should I care?” factor. I was asked that exact question by suburban high school student about 10 years ago while teaching a lesson on isotopes. It was the best question I ever received. And from that point on, all the materials I have created have been based on that pivotal query.
For The Medicine Chest, I wanted to approach the issue from a number of different perspectives. The updated curriculum connects ideas that aren’t really thought of as connected. For instance, nobody really thinks about items that are flushed down the toilet after the handle has been pushed, so why not explore wastewater treatment plants to see what they can filter and what products pass through the system and out to waterways? The lesson named “Wastewater treatment 101: What happens to PPCPs?” does just that. I have also created a lesson using recent research on how PPCPs are changing the normal functionality of aquatic ecosystems. Once the problems are laid out, the curriculum moves on to show how individuals can help reduce the impacts of PPCPs. Finally, as sort of an interesting twist, we look back into the not-so-distant past—turn of the 20th century—to see what kinds of products were used to cure illness and create beauty and how they compare to today’s standards.
I decided to incorporate new teaching techniques into the curriculum. First, the curriculum gives teachers the option to teach each lesson in the conventional way—information gathered in class and followed up by homework—or through a technique called “flipped classrooms.” This model asks students to learn the information, with guidance, the night before and be ready to discuss the topic in class for more in-depth exploration. Second, I applied meta-cognitive thinking to the vocabulary. Third, I abandoned the standard method of testing in favor of essay responses. This technique pairs well with metacognitive thinking and true knowledge because it allows students to express in their own words what they know about the questions being asked. Finally, I aligned the lessons with the Next Generation Science Standards. These new lessons can all be used to lead into the many stewardship-based projects already provided in The Medicine Chest.
One of the challenging aspects of writing curriculum on any emerging topic is that the research is still very new and ever evolving. Once the research is located, many times there are gaps of information about the issue. Then, of course, you have to make the information accessible to different audiences. That is often the most challenging aspect of the work, but it’s all worth it. It’s pleasure to write about emerging issues, and I already have my sights on another topic. I’m excited for the possibilities.
March 9th, 2015 by iisg_superadmin
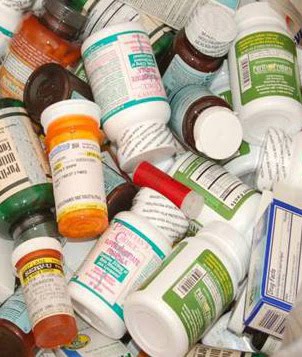 Community medicine collection programs make it easy for people to rid their homes of unwanted pharmaceuticals, but they can be difficult to get off the ground. That’s where our Unwanted Meds team comes in. They have helped police departments across Illinois and Indiana establish collection programs and raise awareness of the importance of proper disposal.
Community medicine collection programs make it easy for people to rid their homes of unwanted pharmaceuticals, but they can be difficult to get off the ground. That’s where our Unwanted Meds team comes in. They have helped police departments across Illinois and Indiana establish collection programs and raise awareness of the importance of proper disposal.
From Rx for Action:
In today’s Community Spotlight feature, we look at West Lafayette Police Department’s Prescription/Over-the-Counter Drug Take Back (Rx/OTC) program. In 2010, Officer Janet Winslow started the wildly successful take-back program, one that has no doubt had a dramatic impact on the community and the environment.
Officer Winslow took a little time out of her busy schedule to answer a few questions for us about the take-back program. And if the work she does here isn’t enough to show what an asset to the community she is, she has also just been named a YWCA Greater Lafayette Woman of Distinction, and will be honored at the “Salute to Women” banquet. Congratulations Officer Winslow!
1. The West Lafayette Police Department collection program started in March 2010. How did this program come about for your area, and why did you decide to take part?
DARE America sent out a request for DARE officers to provide the community with a presentation on Rx/OTC medicines and do a take-back at the same time. I did a community presentation and actually had more people bring me Rx/OTC to be destroyed then that came to the presentation. Since that was successful I asked my Chief if I could try to do it monthly to see how the turnout would be. The “go greener” commission had also expressed and interest to the city government to attempt a take-back.
2. What has been the community’s response? What are people saying about the medicine take-back opportunities and the program?
I do the take-back monthly and every month I think it will be less. I literally have people standing in the police department lobby waiting for me to get my table and boxes set up. It has grown from one small box (~25 pounds) to 6-12 boxes, sometimes over 200 pounds every month. A lot of the people who use my program thank me for providing it to the community.
3. A lot of take-back programs have permanent collection boxes at police departments, but you plan, set-up, collect, and run the entire program (monthly events) yourself. What are some benefits of running a program in this manner?
My chief has asked me several times about getting the permanent box. My answer is always the same: I do not have time daily to check the box. I do not want liquids spilled in the box or broken bottles. Due to a lack of space I started separating the pills from the bottles. I do this as I am taking them back. I then recycle the bottles and the lids are delivered to an organization that makes park benches. I also like the interaction I have with the community during the take-backs.
February 18th, 2015 by iisg_superadmin
A closer look at web tools and sites that boost research and empower Great Lakes communities to secure a healthy environment and economy.
With flu season waning and allergy season on its way, it’s important to keep in mind how to properly dispose of unused and unwanted medicine. IISG’s Unwanted Meds website explains the dangers of flushing or throwing away pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) and provides information, tools, and resources to help individuals, communities, and educators protect aquatic ecosystems.
 The award-winning site contains information on collection programs and events for the Great Lakes region and beyond, as well as a list of commonly accepted and unaccepted items. Instructions for alternative disposal methods are also included for individuals without access to collection programs.
The award-winning site contains information on collection programs and events for the Great Lakes region and beyond, as well as a list of commonly accepted and unaccepted items. Instructions for alternative disposal methods are also included for individuals without access to collection programs.
And visitors looking to prevent PPCP waste will find tips and resources for reducing the amount of unwanted medicine in their homes as well as avoiding personal care products with potentially harmful chemicals.
Local decision makers can take advantage of a free toolkit with instructions for how to safely and legally conduct their own collection program or event. And educators can get help incorporating pollution prevention into their teaching with resources like The Medicine Chest and The Prescription Pill and Drug Disposal (P2D2) Program.
In addition to tips and tools, Unwanted Meds is also host to the latest information on the science behind PPCPs. Its Rx for Action blog discusses leading research on everything from where pharmaceuticals have been detected to how these chemicals impact wildlife to new technologies for removal during wastewater treatment. Readers can also go behind the scenes with the scientists working to make sense of this complicated topic with the UpClose interview series.
For the last information on PPCPs and other emerging contaminants, be sure to follow our pollution prevention team on Twitter, Facebook, Youtube, or Google+.
December 15th, 2014 by iisg_superadmin
University of Illinois students and faculty took a break from the end-of-semester chaos earlier this month to take advantage of a single-day medicine take-back. The student-led event was part of the Learning in Community (LINC) service course facilitated by IISG.
“We spoke to so many different people to put on this event, from police officers to student organization leaders on campus to Jimmy John’s representatives,” said Reema Abi-Akar, a senior in urban planning. “We looked into case studies of past medicine take-back events, learned the ropes, and slowly absorbed all of the components we needed to replicate to put on a successful event.”
“Preparations for the event were challenging,” added Rosalee Celis, project manager and senior in biomedical engineering. “There were various marketing aspects that still had to be completed and communication between a 10-member team over Thanksgiving break was difficult. However, the efforts exerted during this crunch time made the results more satisfying.”
The event was a success, collecting 15 pounds of unused medicine for incineration in just six hours.
 This was just one of the outreach projects led by the LINC students this year. The class, which includes eight students and two undergraduate project managers, also gave an interactive presentation to an ESL class at Urbana High School to raise awareness of the risks of pharmaceutical pollution and the importance of proper disposal.
This was just one of the outreach projects led by the LINC students this year. The class, which includes eight students and two undergraduate project managers, also gave an interactive presentation to an ESL class at Urbana High School to raise awareness of the risks of pharmaceutical pollution and the importance of proper disposal.
“Our group truly feels like we made a difference in the community and spread the word about proper medicine disposal,” Reema said.
And the course has been an eye-opening experience for the students as well.
“To be honest, I started this experience with little to no knowledge about proper medicine disposal,” Reema continued. “All the old medications in my parents’ medicine cabinet were simply collecting dust for years because we never knew how to get rid of them. Once I came into this LINC class and my group began researching the subject further, I became more and more interested in it—and I believe I’m speaking for my entire group as well.
“I can now enter the professional workforce in the pharmaceutical industry with the awareness of potential environmental damage due to pharmaceutical waste,” said Rosalee.
November 13th, 2014 by iisg_superadmin
It’s been two years since our first edition of UpClose, and we decided to celebrate the occasion by taking a behind-the-scenes look at the study that launched an era of scientific and public interest in pharmaceuticals and other emerging contaminants.

And to top it off, we’ve given the award-winning interview series a fresh new look.
Dana Kolpin, a research hydrologist and head of the U.S. Geological Survey Emerging Contaminants Project, played a key role in the first-ever nationwide survey of emerging contaminants. The study found pharmaceuticals, detergents, hormones, and other chemicals in streams across the country. When the results were published in the journal Environmental Science & Technology in 2002, they sparked a of flurry of media and research attention. To this day, in fact, it is still the most cited study in the journal’s history.
In the eighth issue of UpClose, Kolpin looks back on the challenges of designing and conducting a national study—particularly one in search of everyday chemicals like caffeine—and the cutting-edge methods scientists created to analyze the results. He also talks about the gaps in understanding that remain after more than a decade of investigating these contaminants and gives a sneak-peak at USGS’s latest projects.

Find previous issues of UpClose and additional resources at unwantedmeds.org.
October 24th, 2014 by iisg_superadmin
Permanent medicine collection programs make it easy for people to rid their homes of unwanted pharmaceuticals, but they can be difficult to get off the ground. That’s where our Unwanted Meds team comes in. They have helped communities across Illinois and Indiana purchase collection boxes and raise awareness of drop-off programs, including Illinois’ Macon County.
From Rx for Action:
 A few months back, IISG was contacted by Laurie Rasmus of the Macon County Environmental Management Department. She was aware of the issues surrounding improper disposal of pharmaceuticals and wanted to know how we could work together to provide Decatur residents with a convenient way to safely dispose of their unwanted medicines. IISG has found that partnerships like this work really well. So we wanted to start sharing the stories of communities with medicine take-back programs with people who may be thinking about staring a program in their area. Laurie took a few minutes of her time to answer some of our questions about Macon County’s need for prescription take-back boxes and why they are so important to the community.
A few months back, IISG was contacted by Laurie Rasmus of the Macon County Environmental Management Department. She was aware of the issues surrounding improper disposal of pharmaceuticals and wanted to know how we could work together to provide Decatur residents with a convenient way to safely dispose of their unwanted medicines. IISG has found that partnerships like this work really well. So we wanted to start sharing the stories of communities with medicine take-back programs with people who may be thinking about staring a program in their area. Laurie took a few minutes of her time to answer some of our questions about Macon County’s need for prescription take-back boxes and why they are so important to the community.
How did you learn about safe medicine disposal, and how did this initiative come about?
Our department first learned about safe medicine disposal through the one-day take-back collections sponsored by the DEA.
Our office receives many inquiries from residents who want to learn how to dispose of unused and expired medicine in a safe manner that is not harmful to the environment. We informed these residents of the drop-off box operated by the Maroa Police Department. Most were pleased to learn about the Maroa drop-off site but many mentioned that a Decatur-based location would be more convenient. So, we inquired with Illinois-Indiana Sea Grant about the possibilities for a collection site in Decatur and received encouraging information. We then approached Macon County Sheriff Thomas Schneider about a drop-off site at his office. Sheriff Schneider was enthusiastic about establishing a collection box in the lobby of the Macon County Law Enforcement Center.
Why do you think this is an important issue?
Safe, secure medicine disposal reduces the risks of accidental poisonings, drug misuse and pollution.
September 11th, 2014 by iisg_superadmin
Laura Kammin, our pollution prevention specialist, has some exciting news. Let’s let her tell you about it:
If you only had a minute, what would you say?
Just one minute to explain what pharmaceutical waste is and how people can help reduce it. That was the challenge posed by our new pollution prevention team members Erin Knowles and Adrienne Gulley.
Challenge accepted! Here it is, the first installment of the Illinois-Indiana Sea Grant Pollution Prevention Minute.
We know it’s a long name. But don’t worry, the content isn’t. They’re one—ok, maybe sometimes closer to two—minute videos that give easy-to-understand answers to some of the more complicated questions surrounding the use, storage, and disposal of pharmaceuticals and personal care products.
Why videos? We are always getting asked questions like “what happens to the medicine that gets collected?” and “what are microbeads?” We think these new videos are a fun way to share the answers.
And be sure to subscribe to our YouTube channel and watch for the next episode of IISG’s Pollution Prevention Minute.









